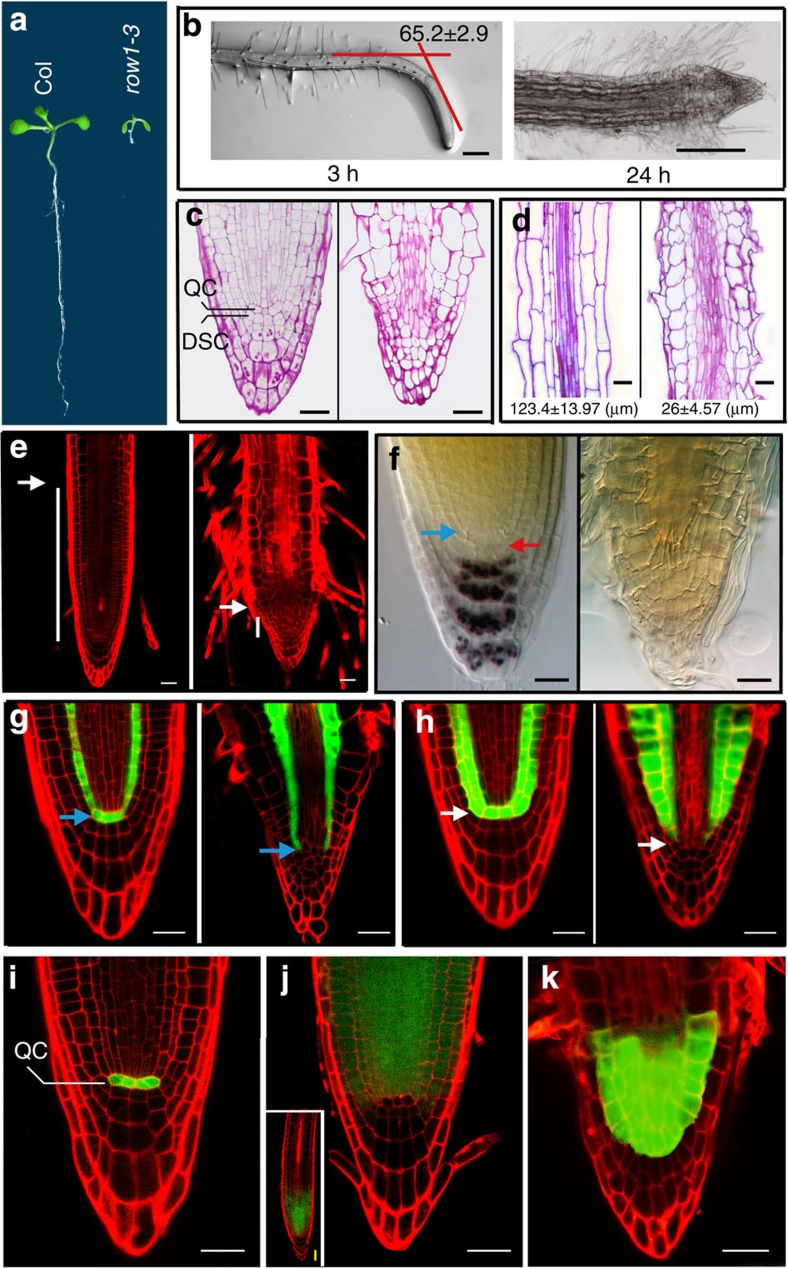
Figure 1. Phenotypic and expression pattern analysis in row1-3 roots.
(a) A 2-week-old wild-type Arabidopsis seedling (Col) showed normal root length (left), whereas a row1-3 root (right) did not elongate. (b) Gravitropic responses in wild-type (left) and row1-3 (right) roots. Degrees of bending (mean±s.e.) were calculated from 10 independent main roots of each type. (c) Median longitudinal semi-thin sections of 7-day-old wild-type (left) and row1-3 (right) root tips stained with periodic acid–Schiff solution. (d) Cell length measurements from maturation zone in wild-type (wt) and row1-3 roots. Root tips from 7-day-old seedlings were used for semi-thin section preparations; cell lengths (mean±s.e. in μm) were obtained from three seedlings of each type. (e) 7-day-old root tips of wild type (left) and row1-3 (right). White bars indicate the size of PM regions. (f) Wild-type root tip accumulated starch granules in columella cells (left), whereas no starch granule was observed in row1-3 root tips (right). Starch granules were stained with the Lugol’s solution and seen as aggregated black spots. Blue arrow, QC position; red arrow, DSC layer. (g) SCR::GFP expression showing normal QC identity (blue bars) in the wild-type (left) and a defective QC position in row1-3 roots (right). (h) Expression pattern analysis of the GFP-enhancer trap line J0571 that show normal QC identity in the wild type (left) with a defective QC in row1-3 roots (right). (i) WOX5::GFP signals were detected specifically in the QC in wild-type seedlings. (j) ROW1::GFP signals were detected above, but not in, the QC position in wild-type seedlings. Inset, a lower-magnification micrograph shows the whole root tip. (k) WOX5::GFP signals were detected in cells above the normal QC position in row1-3 root. Scale bars, 20 μm in this figure.