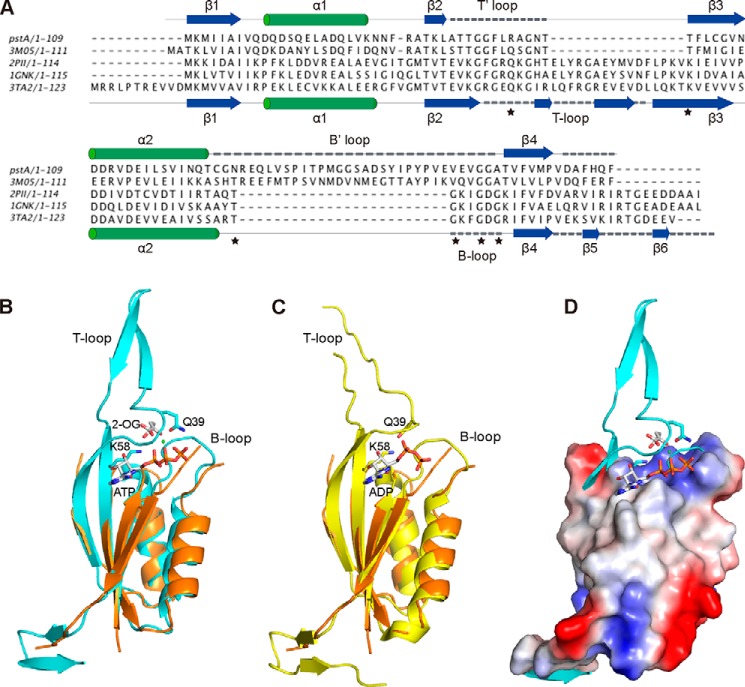
FIGURE 3.
Structural comparison of PstA and classical PII proteins. A, structure-based alignment of PstASA, P. pentosacues ATCC 25745 protein PEPE_1480 (PDB code 3M05), E. coli PII proteins GlnK (PDB code 1GNK), E. coli GlnB (PDB code 2PII), and Archaeoglobus fulgidus PII protein AF_1750 (PDB code 3TA2). The secondary structures for PstASA and 3TA2 are shown above and below the alignment, respectively, with T/T′- and B/B′-loops indicated with dashed lines. Also, the highly conserved PII protein residues Gln-39 and Lys-58 at the base of the T-loop as well as the highly conserved TGXXGDGKI motif within the B-loop of PII proteins are indicated with asterisks. B, overlay of the PstASA monomer structure (orange) in schematic representation with the monomer structure of the A. fulgidus PII protein AF_1750 in the ATP, Mg2+ (green dot), and bound to the 2-OG ligand (PDB code 3TA2); C, overlay with the monomer structure of the A. fulgidus PII protein AF_1750 in the ADP ligand-bound form (PDB code 3TA1) (24). T- and B-loops as well as highly conserved amino acids Gln-39 and Lys-58 (shown in stick representation) as well as ATP, 2-OG, and ADP ligands are labeled in B and C. D, overlay of the surface potential representation of the PstASA protein with the A. fulgidus PII protein AF_1750 and bound ligand in schematic representation.