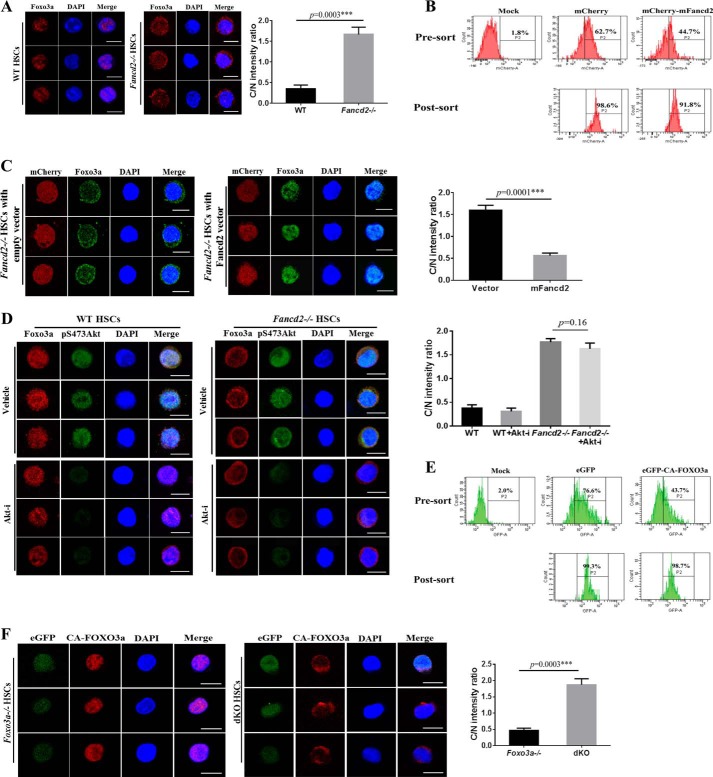
FIGURE 4.
Fancd2 is required for nuclear localization of Foxo3a in HSCs. A, increased cytoplasmic Foxo3a staining in Fancd2−/− HSCs. Left panel, freshly isolated CD34−LSK cells from WT and Fancd2−/− BM were immunostained to detect Foxo3a (red). Nuclei were visualized using DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. Right panel, ratio of fluorescence intensity of anti-Foxo3a staining in cytoplasm (C) and the nucleus (N). B, flow cytometry of mCherry-positive cells before and after sorting. Mock, samples without virus. C, re-expression of Fancd2 restores Foxo3a nuclear localization. Left panel, mFancd2-mCherry or empty-mCherry lentivirus transduced Fancd2−/− CD34−LSK cells were stained with anti-Foxo3a antibody (green) and DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. Right panel, ratio of fluorescence intensity of anti-Foxo3a staining in cytoplasm (C) and the nucleus (N). D, enhanced cytoplasmic localization of Foxo3a in Fancd2−/− HSCs is independent of Akt activation. Left panel, CD34−LSK cells from the WT and Fancd2−/− BM were treated with AKT inhibitor (5 μm) for 2 h. Foxo3a, pS473AKT, and nuclear DNA were visualized by red, green, and blue, respectively. Scale bar, 10 μm. Right panel, quantification of the fluorescence intensity of anti-Foxo3a staining in cytoplasm (C) and the nucleus (N). E, flow cytometry of GFP-positive cells before and after sorting. Mock, samples without virus. F, Fancd2 is required for nuclear retention of the constitutively active CA-FOXO3a in HSCs. Left panel, Foxo3a−/− and Fancd2−/− Foxo3a−/− dKO CD34−LSK cells were transduced with lentivirus expressing the active CA-FOXO3a and eGFP (green). Transduced CD34−LSK cells were staining by anti-FOXO3a antibody (red). Nuclei were visualized by DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. Right panel, quantification of the fluorescence intensity of anti-FOXO3a staining in the nucleus (N) and cytoplasm (C). Each group comprises three to four mice and 20 cells per sample. Akt-i, Akt inhibitor; ***, p < 0.001.