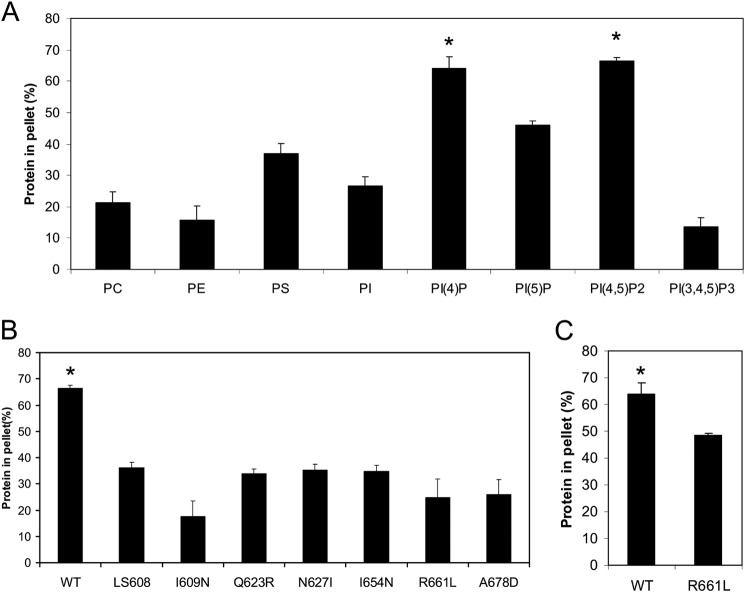
FIGURE 1.
ExoU MLD requires specific residues to bind to PI(4,5)P2. A, recombinant ExoU MLD (residues 503–687) was tested for co-sedimentation in liposome binding assays with various lipids. Liposomes consisting of 30% PC, 20% PE, and 20% cholesterol were supplemented with 30% of the indicated lipids, except for PI(4)P, PI(5)P, PI(4,5)P2, and PI(3,4,5)P3, for which 5% was added (the remaining 25% was PC). Each assay was performed at least in triplicate; values are means, and error bars represent S.E. *, p < 0.05 compared with all other groups. The difference between PI(4)P and PI(4,5)P2 is not significant. PI, phosphatidylinositol. B, recombinant MLD proteins containing single amino acid substitutions (I609N, Q623R, N627I, I654N, R661L, and A678D) or a 5-amino acid insertion (LS608) were tested for binding to PI(4,5)P2-containing liposomes in co-sedimentation assays. Each assay was performed at least in triplicate; values are means, and error bars represent S.E. WT indicates the wild-type MLD of ExoU, using the PI(4,5)P2 binding data depicted in A. *, p < 0.001 compared with each variant. No difference between the variants is statistically significant. C, recombinant wild-type (WT) and R661L MLD protein were analyzed for binding to PI(4)P-containing liposomes. *, p < 0.05 relative to R661L variant.