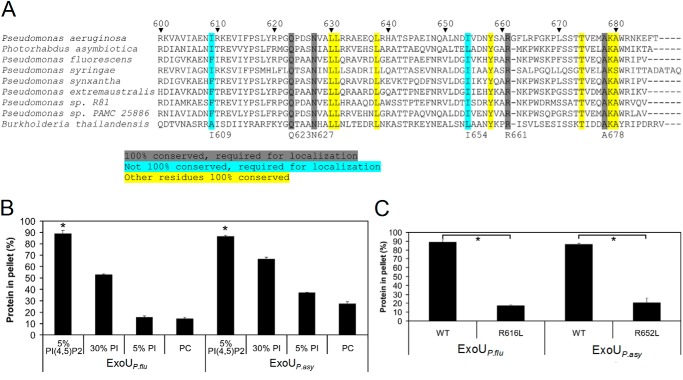
FIGURE 3.
Several residues necessary for the binding of ExoU to PI(4,5)P2 are conserved in other proteins containing ExoU MLD-like domains. A, alignments of proteins containing ExoU MLD-like domains. The highlighted sequences identify highly conserved residues. Those residues highlighted in gray and blue were critical for ExoU localization in mammalian cells (30) and for binding to PI(4,5)P2-supplemented liposomes (Fig. 1B). Numbering system refers to ExoU of P. aeruginosa. Accession numbers for the indicated proteins in order are as follows: O34208, YP_003039880.1, YP_006326405.1, ZP_07262921.1, ZP_10142741.1, ZP_10438440.1, ZP_11185695.1, ZP_10426928.1, and ZP_18329767.1. B, recombinant putative MLD proteins from ExoUP. flu and ExoUP. asy (residues 453–639 and 495–676, respectively) were purified and assayed for liposome binding. Liposomes consisted of the same composition as depicted in Fig. 1, except that 5% PI/25% PC-supplemented liposomes were also tested. C, arginine-to-leucine substitutions corresponding to R661L in ExoUP. aer were generated in ExoUP. flu and ExoUP. asy recombinant MLD proteins. These proteins were purified and were tested for binding to liposomes supplemented with 5% PI(4,5)P2. The results for “WT,” which refers to wild-type protein, are the same as depicted in B. Each assay was performed in triplicate; values are means, and error bars represent S.E. *, p < 0.001 for PI(4,5)P2 compared with other lipids and wild-type compared with arginine-to-leucine substitution proteins.