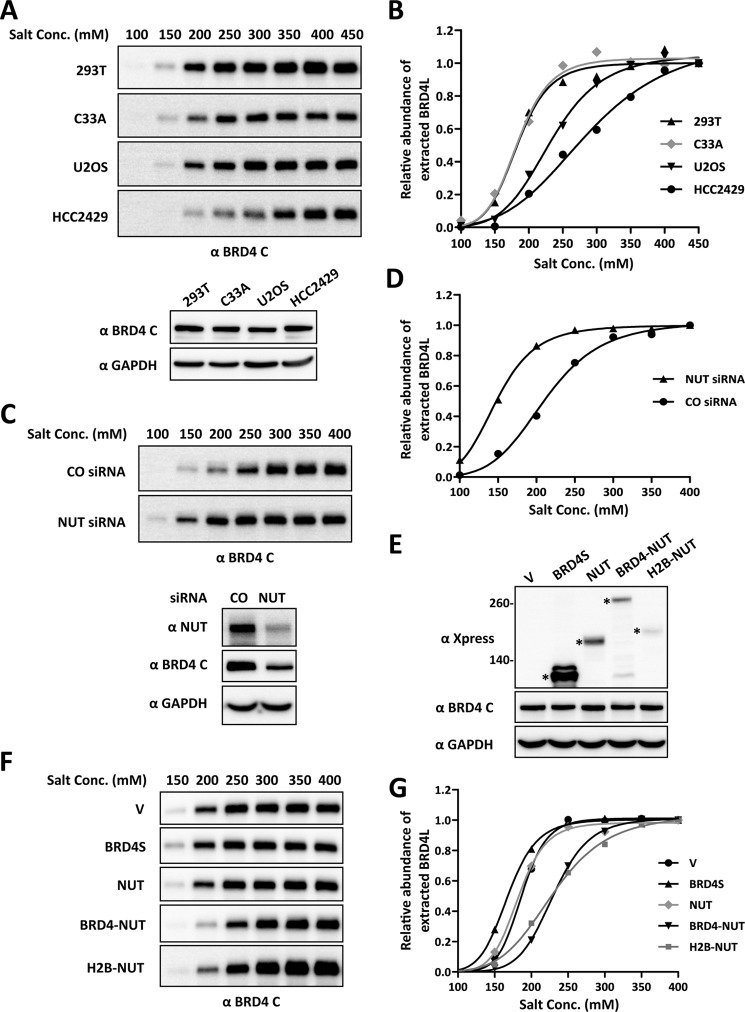
FIGURE 4.
Expression of BRD4-NUT increases the binding of BRD4 to chromatin. A, nuclear proteins from four different cell lines (293T, C33A, U2OS, and HCC2429) were extracted with different NaCl concentrations (Conc., 100–450 mm). Nuclear extracts were immunoblotted with the BRD4 C antibody. The concentration of nuclear proteins extracted with 450 mm NaCl buffer was determined by Bradford assay, and 20 μg of proteins was immunoblotted with BRD4 C and GAPDH antibodies to compare endogenous BRD4 levels in these cell lines. B, the intensity of BRD4 bands was quantified using ImageJ. The relative abundance of extracted BRD4 was calculated by setting the intensity of the BRD4 band from 450 mm NaCl extraction as 1. The curves were fit using GraphPad Prism software. C, HCC2429 cells were transfected with a non-targeting control (CO) or NUT siRNA. 36 h post-transfection, nuclear proteins were extracted with different NaCl concentrations (100–400 mm) and immunoblotted with the BRD4 C antibody. The concentration of nuclear proteins extracted with 400 mm NaCl buffer was determined by Bradford assay, and 20 μg of proteins was also immunoblotted with NUT, BRD4 C, and GAPDH antibodies to confirm the NUT knockdown efficiency. D, same as B, except the intensity of the BRD4 band from 400 mm NaCl extraction was set as 1. E, 293T cells were transfected with vector control (V) or constructs expressing Xpress-tagged BRD4S, NUT, BRD4-NUT, or H2B-NUT. 24 h post-transfection, whole cell lysates were immunoblotted with Xpress, BRD4 C, and GAPDH antibodies. The concentration of cell lysates was determined by Bradford assay, and 20 μg of proteins was loaded for each lane. Asterisks indicate the Xpress-tagged proteins. F, 293T cells were transfected as in E. 24 h post-transfection, nuclear proteins were extracted with different NaCl concentrations (150–400 mm) and immunoblotted with the BRD4 C antibody. G, as described in D.