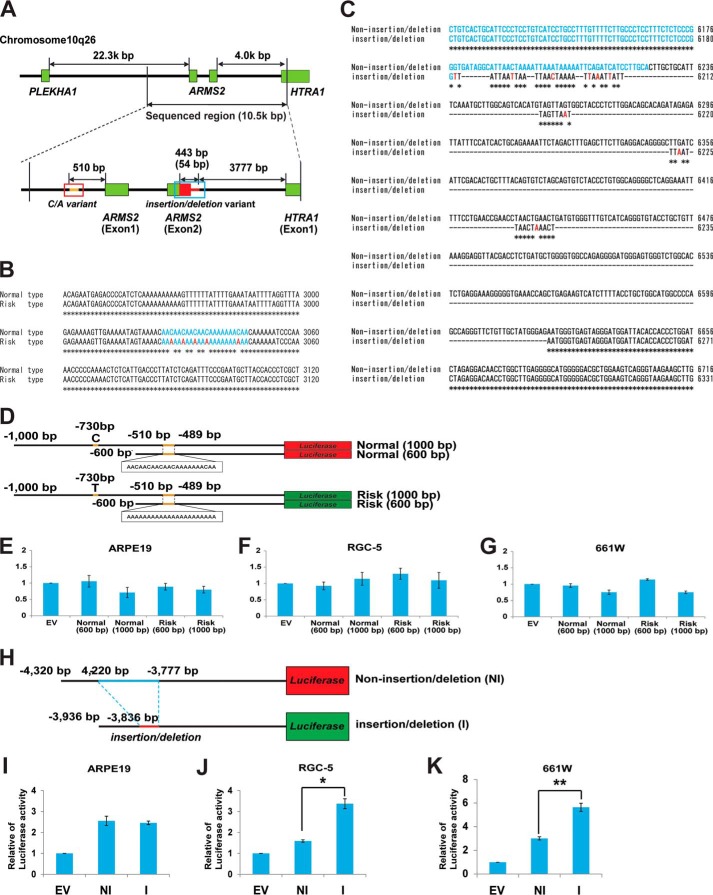
FIGURE 1.
Transcription regulatory region of ARMS2 and HTRA1. A, a schematic diagram of the transcription regulatory region of ARMS2 and HTRA1. Sequencing of the indicated transcription regulatory region spanned 10.5 kbp and was performed for both AMD and non-AMD controls. Two unique sequences, a C/A repeat variant in the ARMS2 transcription regulator (indicated with a blue box) and an insertion/deletion variant downstream of exon 2 of ARMS2 (indicated with a red box), were identified in a patient with AMD that carried the SNP, rs10490924. B, characteristic C/A mutations present in the ARMS2 transcription regulatory region (blue, C/A variant; red, C to A substitution). C, the insertion/deletion mutations present in the HTRA1 transcription regulatory region (blue, ARMS2 exon 2 region; red, point mutations). D–G, analysis of ARMS2 transcription regulator activity using a luciferase assay system. D, four luciferase vectors were generated to analyze ARMS2 transcription regulator activity: normal (1,000 bp), normal (600 bp), risk (1,000 bp), and risk (600 bp). The 1,000-bp sequence contained a C/T SNP in the upper 730-bp region from ARMS2 exon 1. ARMS2 transcription regulator activity detected in ARPE19 cells (E), RGC-5 cells (F), and 661W cells (G). Error bars, S.D. H–K, HTRA1 transcription regulator activity detected in various retinal cell lines. H, schematic diagram of the ARMS2-HTRA1 constructs used in the luciferase assays performed (black line, common regulator sequence; blue line, non-insertion/deletion regulator unique sequence; red line, insertion/deletion regulator unique sequence). Full-length HTRA1 transcription regulator activity detected in ARPE19 cells (I), RGC5 cells (*, p = 7.5 × 10−6) (J), and 661W cells (**, p = 1.07 × 10−6) (K). Error bars, S.D. EV, empty vector; NI, non-insertion/deletion regulator; I, insertion/deletion regulator.