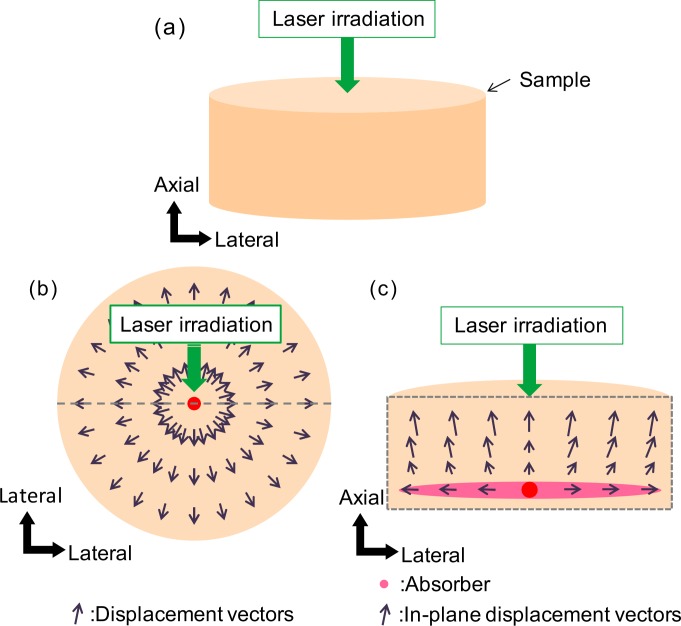
Fig. 1.
(a) The biological sample is modeled as a cylindrical shape. The coagulation laser is applied at a particular position on the sample. (b) The top cross-sectional view of the sample. The thermal expansion/contraction is modeled as axially-symmetric radial displacements in the x–y plane. (c) The side cross-sectional view of the sample. The thermal expansion/contraction is modeled as in-plane displacements in the x–z plane. The black arrows indicate the displacement vectors. The pink ellipse indicates the main absorber of the sample.