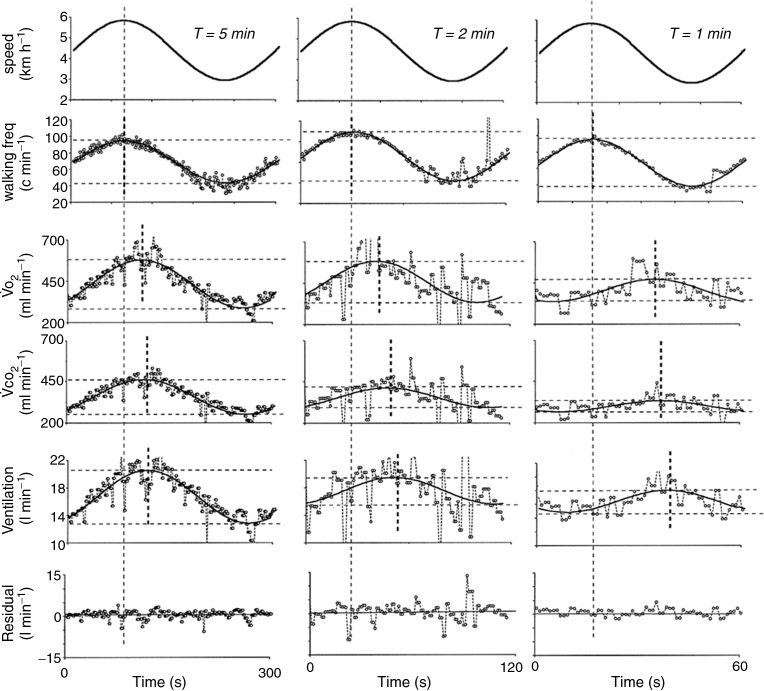
Figure 2.
As the period of change in walking speed decreases, the pulmonary gas exchange response becomes dissociated from the motor activity due to a slower time constant response than the locomotor activity, which follows very precisely the change in walking speed. Minute ventilation follows the change in pulmonary gas exchange, with a reduction in amplitude and an increase in phase lag despite unchanged locomotor and motor control. Similar results have long been reported in humans during cycling exercise (Casaburi et al. 1977).