Figure 3.
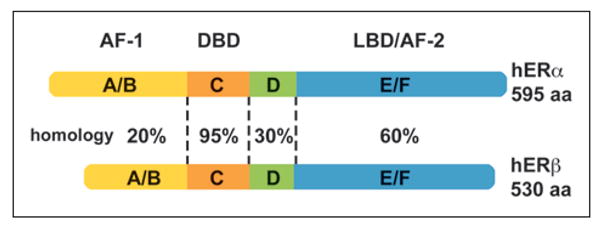
Non-homologous domains/regions within human nuclear estrogen receptors (hERs) contribute to dissimilarities in transcription. Although ERα and ERβ are highly homologous (95%) within the DNA binding domain (DBD), ERα has greater transcriptional activity. Differences in the ligand binding domain (LBD) contribute to increased affinity of 17β-estradiol (E2) for ERα. Furthermore, differences in the structure of the activation function regions (AF-1 and AF-2) influence the ability of transcriptional co-regulators to interact with the receptors.
