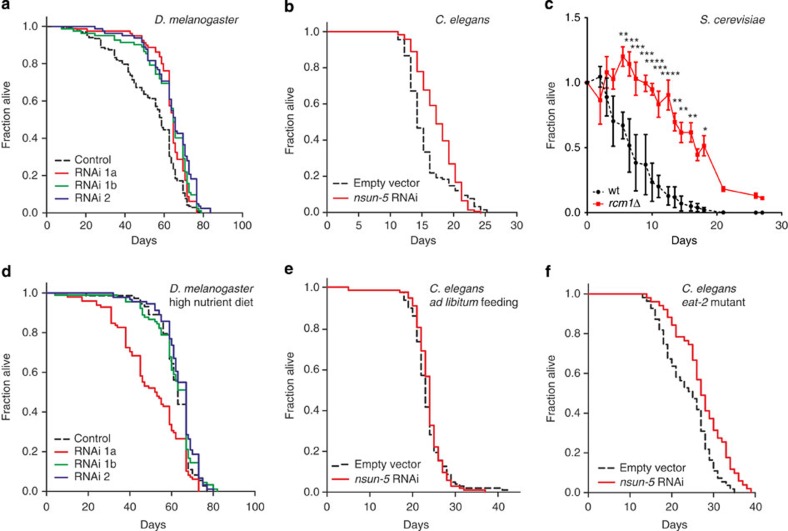
Figure 2. NSUN5 modulates animal lifespan depending on feeding conditions.
(a) Two individual RNAi constructs of dNsun5 extend the lifespan of D. melanogaster in three RNAi lines (average N per group=78, log-rank with Holm–Sidak pairwise comparisons, P<0.001 for all three constructs). (b) nsun-5 RNAi in C. elegans NL2099 results in increased lifespan (N=335, log-rank, P<0.001). (c) Deletion of RCM1 in haploid S. cerevisiae increases chronological lifespan in water. Error bars represent s.e.m. of three biological replicates (multiple comparison adjusted two-way ANOVA with Sidak post test, α=0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001). (d) D. melanogaster lifespan is not extended by two different dNsun5 RNAi constructs in three different lines using high yeast and sugar diet (average N per group=84, log-rank not significant except RNAi 1a versus control P=0.01). (e) nsun-5 RNAi in NL2099 C. elegans does not result in increased lifespan when ad libitum (AL) fed (average N per group=120, log-rank not significant). (f) The lifespan of DA1116 harbouring an eat-2 mutation is further extended by nsun-5 RNAi (average N per group=120, log-rank P=0.001).