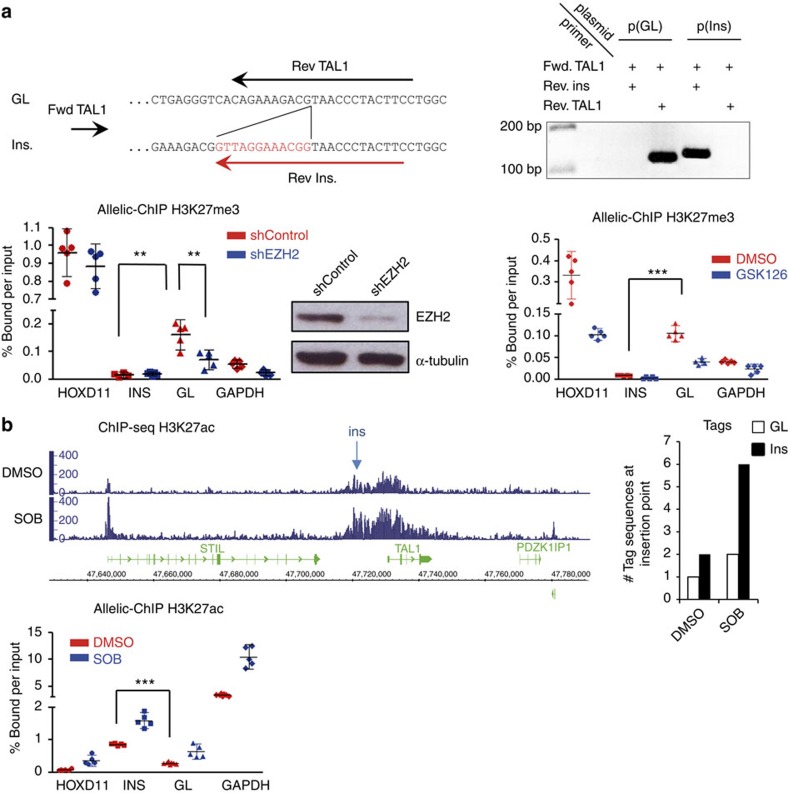
Figure 2. Site- and allele-specific analysis of histone methylation/acetylation marks at the insertion breakpoint in Jurkat.
(a) Allelic-ChIP assay of H3K27me3 marks. Top panel: the assay to discriminate the germline (GL) from the inserted allele (Ins.) by substituting one of the GL primers allowing detection of the GL configuration at the insertion site (Rev. TAL1), with an insertion-specific primer allowing detection of the inserted configuration (Rev. Ins, overlapping the 12-bp insertion). Primer pairs were tested on GL p(GL) or inserted p(Ins) cloned fragments (and on cell lines containing (Jurkat) or not (DND) the insertion) to exclusively amplify each configuration, and do not crossreact. Bottom middle panel: western blot of EZH2 protein content on shMock or EZH2 knockdown conditions. Allelic-ChIP assays were performed in presence of a non-silencing sh-RNA (shControl) or a sh-RNA-targeting EZH2 (shEZH2) (left panel) or after the incubation of Jurkat cells with GSK126 (0.5 μM, 72H) or vehicle (dimethyl sulphoxide, DMSO; right panel). GAPDH and HoxD11 were used as controls for activated/repressed genes, modulated according to the polycomb-dependent H3K27me3 marks. Note that EZH2 knockdown/inhibition triggered only partial decrease of H3K27me3 marks at the PcG-repressed HoxD11 control gene, possibly due to incomplete knockdown/inhibition and/or redundancy of polycomb components in the adult lymphoid lineage42. (b) Enrichment of acetylation marks at the TAL1 locus. H3K27Ac ChIP was performed with Jurkat cells incubated with vehicle (DMSO) or the histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium butyrate (SOB) (5 mM, 4H); DNA was then analysed by ChIP-seq (left panel) or by allelic-ChIP (bottom panel). For the ChIP-Seq, quantification of the number of tag sequences at the insertion point is shown (right panel). ***P<0.001; **P<0.001; *P<0.05, unpaired t-test. Errors bars represent 95% confidence interval.