Figure 8.
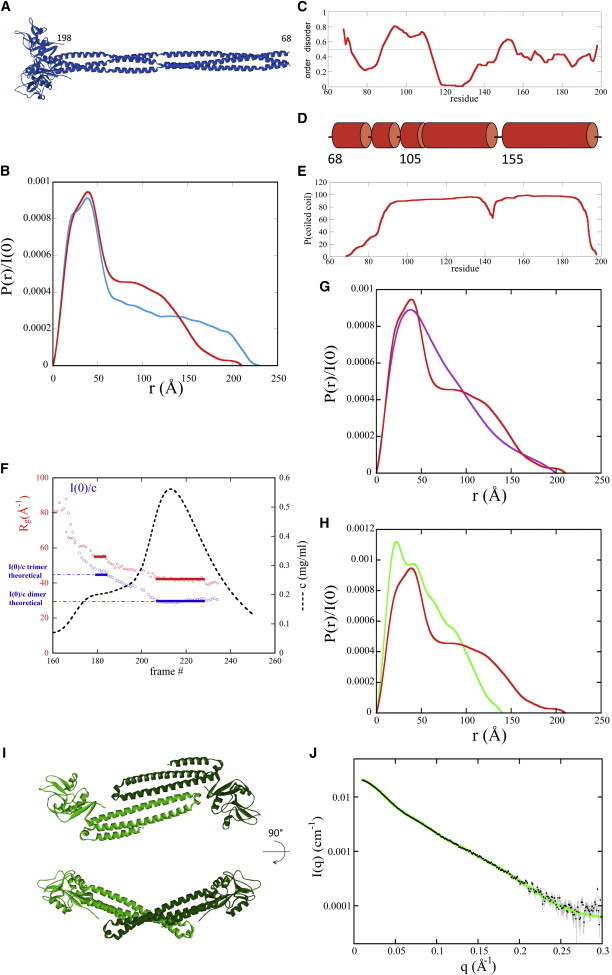
SAXS analysis. (A) Model of Lg-ECDWT trimer from (30) after incorporation of the trimeric head and proximal coiled-coil region from 3KQG. (B) Comparison of the distance distribution function of Lg-ECDWT model shown in A (cyan line), with that derived from the experimental curve for Lg-ECDWT (red curve). (C) Disorder prediction using PondR (30) in the range 68–198 (neck). (D) Prediction of secondary structure in the same range. Only helices are predicted. (E) Prediction of coiled coil using Logicoil (31). (F) Variation along the SEC elution profile of the protein concentration c (black dashed line), radius of gyration Rg (red diamonds), and I(0)/c (blue squares). Each frame corresponds to a 2 s SAXS pattern. (G) Comparison of the distance distribution functions of the WT trimer (red line) and of the trimer of F241L mutant (purple line). (H) Comparison of the distance distribution functions of the WT trimer (red line) and of the dimer of F241L mutant (green line). (I) Two 90° rotation views of a typical model obtained with SASREF for the dimer of F241L mutant. (J) Black dots: SAXS experimental data for the dimer of F241L mutant with error bars (gray lines); for q < 0.17 Å−1 error bars are smaller than the black dots; green line: calculated curve using CRYSOL from the model shown in Fig. 8I.
