Figure 6. Wnt11-CreER expression terminates in the embryonic endoderm and the extra-embryonic vasculature shortly after gastrulation.
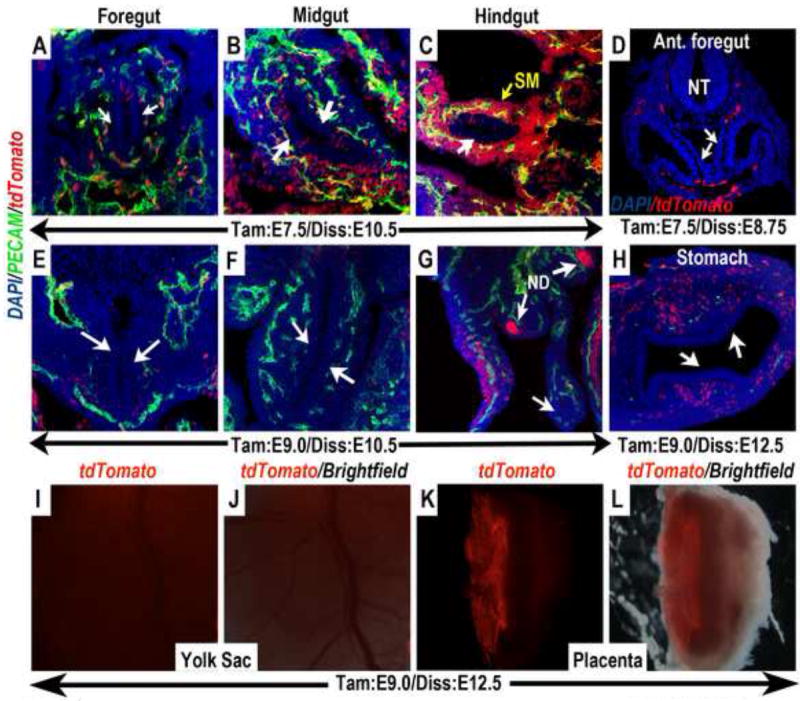
(A-D) In embryos in which a single dose of tamoxifen was administered at E7.5, the contribution of tdTomato expressing cells to the mid- (B) and hindgut (C) endoderm was reduced, and could no longer be found in the foregut endoderm (A & D). In contrast, abundant contribution of tdTomato expressing cells could be found in the splanchnic mesenchyme (SM) surrounding the hindgut (C) and various vasculature. (E-L) When tamoxifen was administered at E8.5-9.0, tdTomato expressing cells were completely absent from the foregut (white arrows in E and H), midgut (white arrows in F) and hindgut (white arrow in G) endoderm, but contributed specifically to the nephric duct (ND in G). The contribution of tdTomato expressing cells to the extra-embryonic vasculature in the yolk sac and placenta was also diminished. (I) Whole mount epi-fluorescence alone, and (J) merged image with brightfield revealed no tdTomato expressing cells in the yolk sac. (K and L) Bisection of the placenta revealed that tdTomato expressing cells also could no longer be found in the fetal vasculature (compare to Fig.4C-D”). The limited remaining tdTomato expression appeared to be in the extra-embryonic Reichert’s membrane. ND (nephric duct); NT (neural tube); SM (splanchnic mesenchyme).
