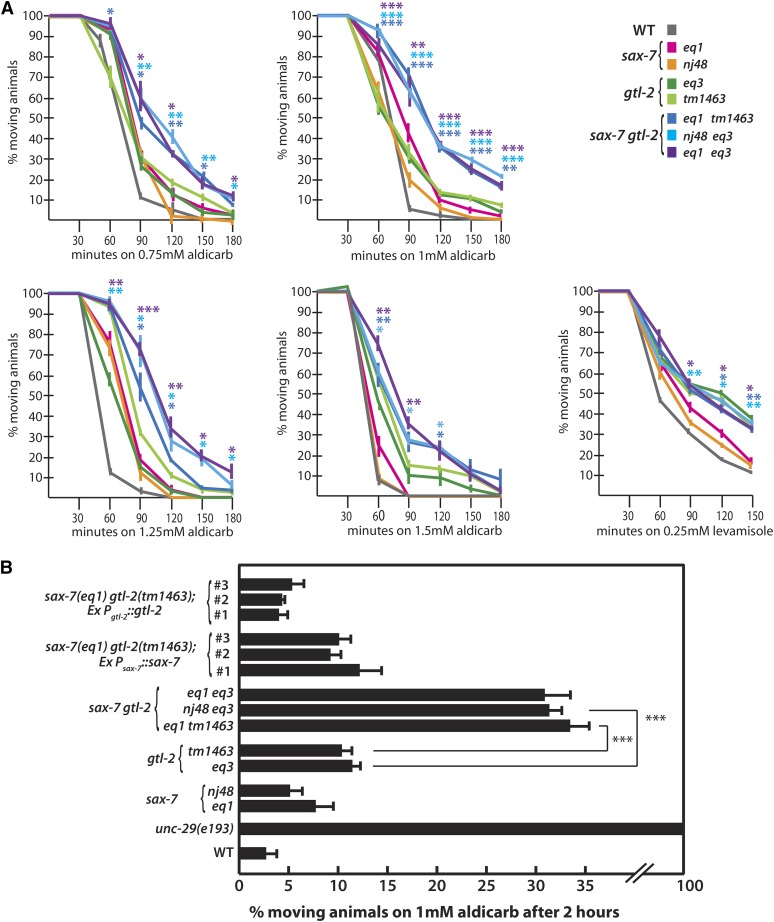
Figure 2.
The response of sax-7gtl-2 as well as sax-7 and gtl-2 single-mutant strains to the cholinesterase inhibitor, Aldicarb, and the acetylcholine receptor agonist, Levamisole. (A) A time-course response of wild-type and mutant strains on NGM media containing 0.75, 1, 1.25, or 1.5 mM Aldicarb and 0.25 mM Levamisole. Controls include wild type (WT), which is sensitive to Aldicarb and Levamisole, and unc-29(e193), which is resistant to Aldicarb and Levamisole (data not shown) (Miller et al. 1996; Fleming et al. 1997). The color-coded *’s in the Aldicarb assays represent the P-values calculated by Student’s t-test comparing sax-7gtl-2 Aldicarb resistance to the corresponding gtl-2 allele. On the other hand, the color-coded *’s in the Levamisole assays represent the P-values when comparing sax-7gtl-2 Levamisole resistance to the corresponding sax-7 allele. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0001. (B) The percentage of animals moving after a 2-hr exposure to 1 mM Aldicarb. Transgenes containing wild-type gtl-2 can consistently suppress the Aldicarb resistance exhibited by sax-7gtl-2 double mutants. Similarly, transgenes containing wild-type sax-7 restore the level of resistance of the double mutant to that of the gtl-2 single mutant. Three independent transgenic lines were analyzed for each construct assessed. Error bars show the standard error of the mean of at least 12 sample sets, where n = 25 animals for each set.