Figure 2.
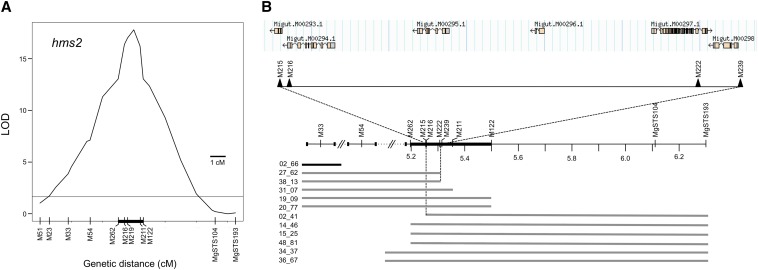
Genetic dissection and physical map of the hms2 locus in Mimulus. (A) QTL profile generated from informative hms2 F2 recombinants that also carry at least one M. guttatus allele at hms1. The positions of molecular markers are indicated along the bottom. Hybrid male sterility effects were mapped to an interval of roughly 1 cM between M216 and M211. The thick black bar along the x-axis indicates a 2-LOD drop on either side of the peak, corresponding to 1.6 cM. The horizontal line at 1.65 shows the 5% significance LOD threshold generated using 1000 permutations. (B) Progeny testing for a subset of the informative hms2 recombinants further refined the sterility locus. The hms2 F2 recombinants are shown with horizontal bars representing heterozygous genotypes (regions left blank indicate markers homozygous for M. nasutus alleles). Because all of these individuals carry at least one M. guttatus allele at hms1, they are sterile if they are also homozygous for M. nasutus alleles at hms2. Black bar indicates a male-sterile individual and shaded bars indicate male-fertile individuals. (Note that the larger number of male fertiles reflects a bias in seed production between these phenotypic classes; we were more likely to collect seeds from male-fertile recombinants.) Physical locations of genetic markers (∼1 Mb shown) map hms2 to a region of only 60,052 bp (between markers M215 and M239) that includes five predicted genes. Annotation is based on M. guttatus Annotation v2.0, phytozome.net (M. guttatus v1.1 assembly scaffolds are separated by dotted lines with double hash marks).