Fig. 5.
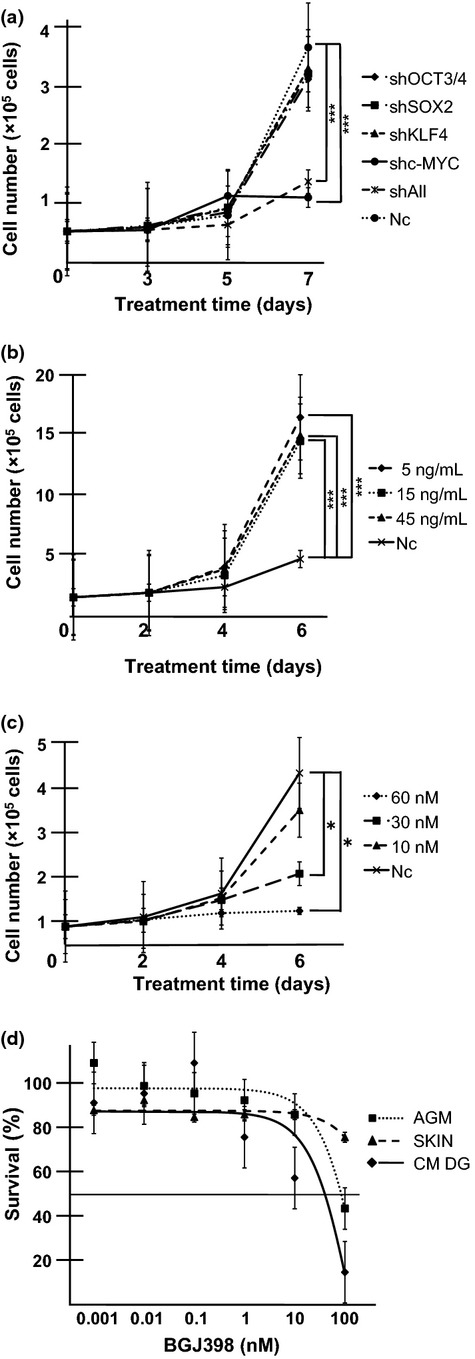
Dependence of common marmoset dysgerminoma-like (CM DG) cell growth on c-MYC and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) signaling. (a) Inhibition of CM DG growth by knockdown of c-MYC. Cells (3 × 104) were seeded on 24-well plates and transduced with shRNA targeting OCT3/4, SOX2, KLF4, c-MYC, or all reprogramming factors (shAll). Cell growth curves were analyzed by cell counts at the indicated time points. Results are shown as means ± SD. ***P < 0.001. Nc, negative control (mock vector). (b) Growth rate of CM DGs was promoted by the addition of bFGF. Cells were cultured in the presence or absence (Nc) of bFGF. Cell numbers were counted at the indicated time points. Results are shown as means ± SD. ***P < 0.001. (c) FGFR inhibitor suppressed CM DG growth. Cells were cultured in the presence or absence (Nc) of the FGFR1-4 inhibitor BGJ398; bFGF was added at 5 ng/mL. Cell numbers were counted at the indicated time points. Results are shown as means ± SD. *P < 0.05. (d) CM DGs, aorta-gonado-mesonephros fibroblasts (AGM), and CM skin fibroblasts (SKIN) were treated with different concentrations of BGJ398 for 3 days, and the growth-inhibitory effects were analyzed by MTS assay. The IC50 for CM DGs was lower than those for parental AGM fibroblasts and control CM skin fibroblasts. Results are shown as means ± SD.
