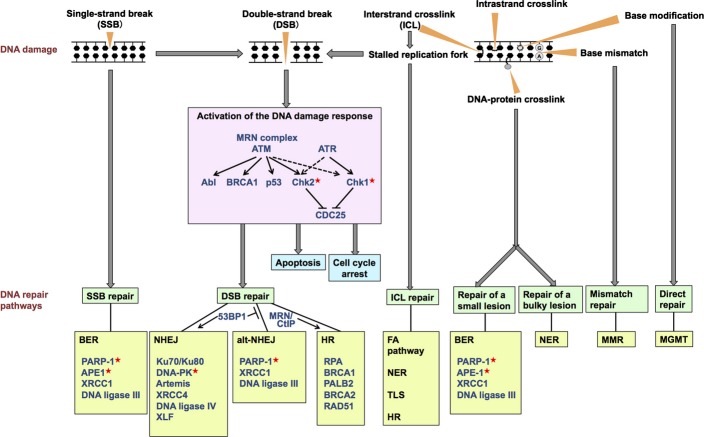
Fig. 1.
Overview of the diverse spectrum of DNA damage and the DNA damage response. The major repair pathways and key proteins used to process each type of damage are shown. In non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ), the Ku70/Ku80 complex binds to the DNA double-strand break ends and recruits the other indicated components. In base-excision repair (BER), poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) detects and binds to single-strand breaks and ensures accumulation of other repair factors at the breaks. Single-strand breaks containing modified DNA ends are recognized by damage-specific proteins such as apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease (APE1), which subsequently recruits Polβ and XRCC1-DNA ligase IIIα to accomplish the repair. All the molecules indicated here are aberrated in sporadic cancers. The proteins targeted for cancer therapy in the present clinical trials are marked with red asterisks. alt-NHEJ, alternative NHEJ; ATM, ataxia telangiectasia mutated; ATR, ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related; FA, Fanconi anemia; HR, homologous recombination; MGMT, O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase; MMR, mismatch repair; MRN, MRE11–RAD50–NBS1; NER, nucleotide excision repair; TLS, translesion synthesis.