Fig. 2.
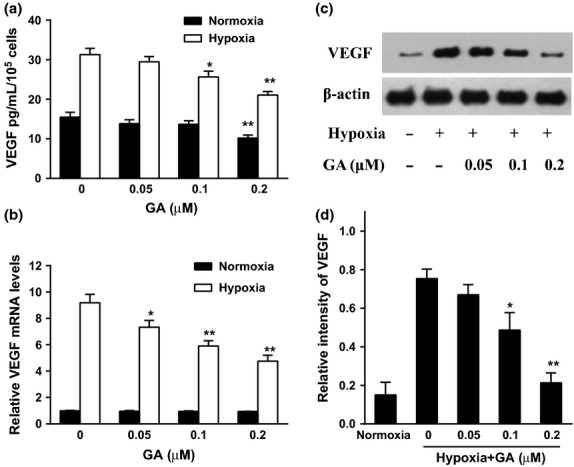
Effect of gambogic acid (GA) on the secretion and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in U266 cells under normoxia and hypoxia. (a) U266 cells were treated by GA (0, 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 μM) for 8 h under normoxia and hypoxia. VEGF secretion was detected by ELISA assay. Bars were the mean ± SD (n = 3). The comparisons were made relative to untreated controls, and the different levels of significance were indicated as *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. (b) Effect of GA on VEGF mRNA level under normoxia and hypoxia. U266 cells were treated with various concentrations of GA (0, 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 μM) for 4 h under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. VEGF mRNA was detected by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and analyzed by the ΔΔCt method. Bars were shown as mean ± SD (n = 3) and represent VEGF/β-actin fold relative to the untreated group. The different levels of significance were indicated as *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. (c) Effect of GA on VEGF protein expression under normoxia and hypoxia. U266 cells were treated with various concentrations of GA (0, 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 μM) for 4 h under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. VEGF protein expression was analyzed by western blots. (d) For quantity of (c), images were analyzed using Image J. Bars are the mean ± SD (n = 3). The comparisons were made relative to hypoxia alone group, and the different levels of significance were indicated as *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.
