Fig. 6.
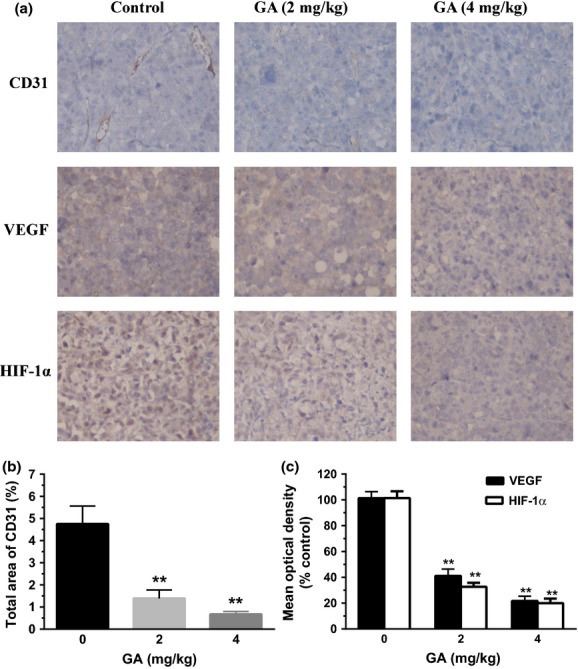
Gambogic acid (GA) inhibited tumor angiogenesis in U266 xenograft mouse model. (a) Immunohistochemistry was performed in tumor sections with antibodies of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and CD31. The result showed a remarkable decrease in expression of HIF-1α, VEGF and CD31 in the treated groups with 2 and 4 mg/kg GA compared with untreated control groups. (b) To identify the tumor angiogenesis, the stained area of CD31 in 10 fields was quantified by using Image Pro Plus. Bars are the mean ± SD (n = 10). The comparisons were made relative to untreated controls, and the different levels of significance was indicated as **P < 0.01. (c) The images were quantified using Image Pro Plus and mean optical densities (of control) of VEGF and HIF-1α were shown. Bars are the mean ± SD (n = 10). The comparisons were made relative to untreated controls, and the different levels of significance was indicated as **P < 0.01.
