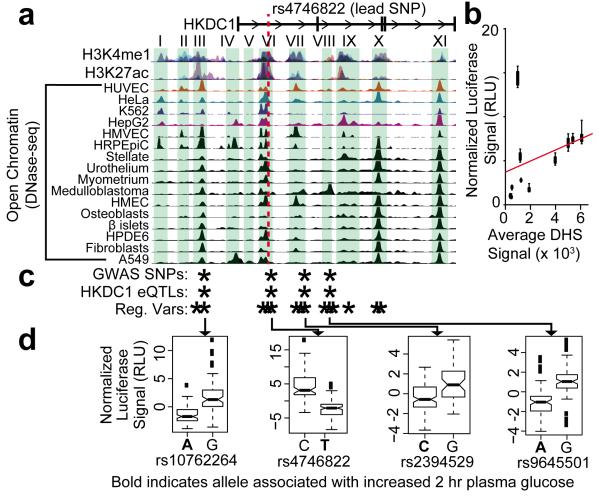
Figure 1. Coordinated allelic regulation of HKDC1.
(a) Map of chromatin landscape and the HKDC1 genome wide association (GWA) locus target regions. Evidence of active regulatory elements – genomic regions with the covalent histone modifications H3K4me1 and H3K27ac as measured by ChIP-seq and open chromatin measured by DNase-seq – is shown across the genomic locus associated with gestational hyperglycemia. Green boxes indicate candidate the regulatory elements whose activity was measured with luciferase reporter assays. Histone modification and open chromatin data were obtained from the ENCODE project. (b) For each regulatory element in a, the enhancer activity (y-axis) is plotted against DNase-seq signal averaged across the element (x-axis) in HepG2 cells (n= 8 to 19). Enhancer activity was determined by dividing the relative luciferase signal from the most active haplotype by that of a control vector with the same promoter but no enhancer. The red line indicates the Pearson correlation between DNase-seq signal and enhancer activity. Error bars show standard deviation (s.d.). (c) Coordinated regulatory variation in the HKDC1 locus. SNPs that are significantly associated with gestational hyperglycemia (“GWA SNPs”), HKDC1 mRNA expression (“HKDC1 eQTLs”), or regulatory activity in allele-specific luciferase reporter assays (“Reg. Vars”) are marked with an asterisk. (d) Example box plots showing allele specific regulatory activity for the four SNPs that were significantly associated with gestational hyperglycemia, HKDC1 expression, and luciferase reporter gene expression. In each example, they associated with increased 2 hr plasma glucose are shown in bold face. The bottom and top boxes are the first and third quartiles, and the band inside the box is the median. The ends of the whiskers represent the lowest and highest data points within 1.5 interquartile range of the lower and upper quartiles. Black squares represent outliers defined as 1.5 times the interquartile range above the upper quartile or below the lower quartile. The number of replicate measurements followed by each allele are as follows: 103 of rs10762264A, 79 of rs10762264G, 80 of rs4746822C, 115 of rs4746822T, 129 of rs2394529C, 47 of rs2394529G, 80 of rs9645501A, and 80 of rs9645501G.