Figure 5.
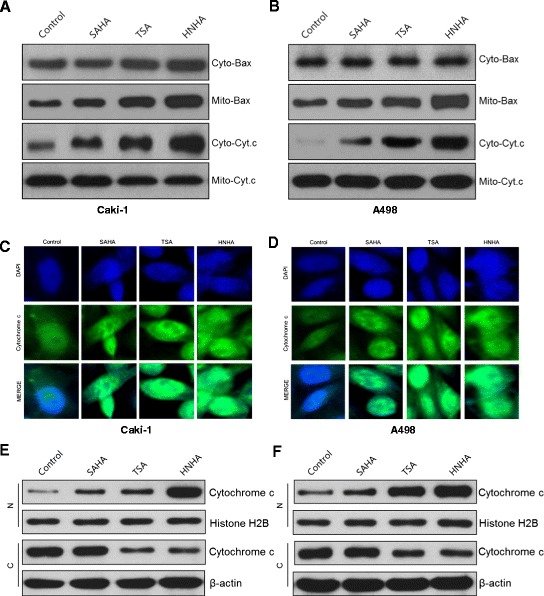
HNHA induced cytochrome c-dependent, caspase-dependent apoptotic death in RCCs. Subcellular fractionation showed that the Bax level was increased, and cytochrome c release into the cytosol was enhanced by HNHA, in Caki-1 (A) and A 498 cells (B). Immunofluorescent cytochemical staining showed that cytochrome c was translocated and accumulated in the nucleus, suggesting that HNHA induced apoptosis through a cytochrome-c-dependent pathway. (C, D) Western blot analysis after subcellular fractionation confirmed that cytochrome c was translocated into the nucleus after HNHA treatment (E, F).
