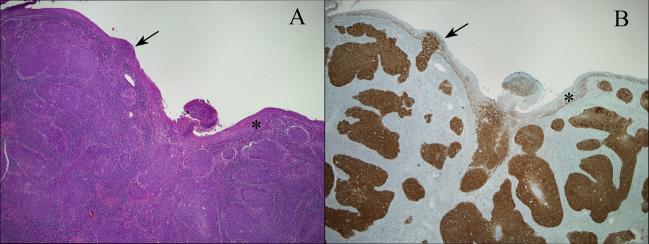
Figure 2.
HPV-related squamous cell carcinomas of the oropharynx typically target the tonsillar crypts (A, hematoxylin and eosin stain). The epithelium lining the surface of the tonsils (asterisks) is usually uninvolved by malignant or premalignant changes. When the surface epithelium is involved, it is usually be secondary extension from the crypts with an abrupt transition between tumor and normal epithelium (arrows). P16 immunohistochemistry allows visualization of HPV distribution in the tonsils (B, p16 immunohistochemical stain).