Fig. 3.
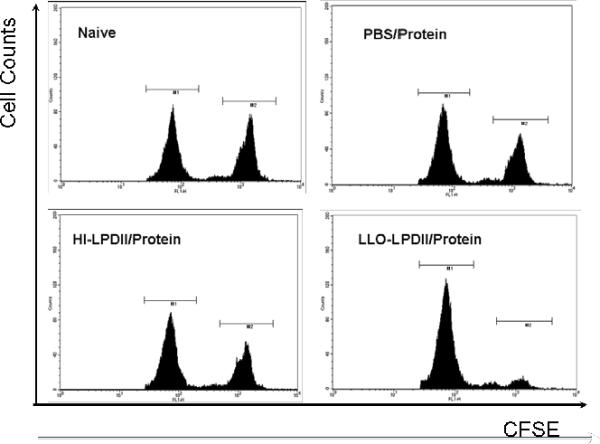
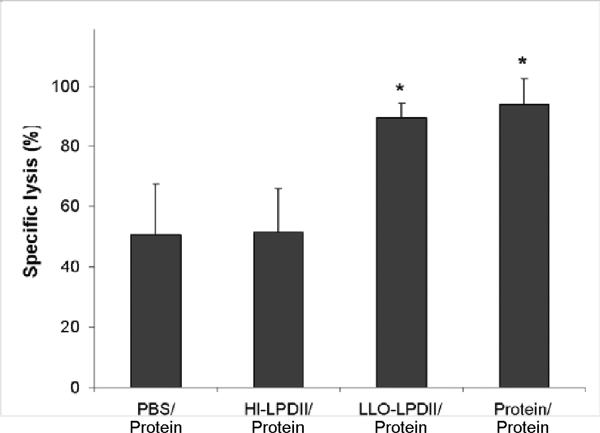
Enhanced functional cytolytic CD8+ T cells were detected in LLO-LPDII-primed mice by an in vivo CTL assay. (A) C57BL/6 mice were primed subcutaneously with PBS, 50 μg of OVA protein encapsulated in LLO-containing liposomes, 50 μg of pNGVL3.OVA in LLO-LPDII or in HI-LPDII, respectively. 12 days post-prime, all of the mice were boosted with 50 μg of OVA protein encapsulated in LLO-containing liposomes. 12 days post-boost, mice were i.v. injected with an equivalent amount of SIINFEKL-pulsed (labeled with 4 μM CFSE; CFSEhigh) and non-pulsed (labeled with 0.4 μM CFSE; CFSElow) splenocytes obtained from syngeneic naive donor mice. 16 hr after adoptive transfer of CFSEhigh and CFSElow cells, spleen cells from the recipient mice were harvested, and the proportions of the CFSEhigh and CFSElow cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Representative flow cytometry data show counts of remaining non-pulsed CFSElow splenocytes (left peak) versus remaining SIINFEKL-pulsed CFSEhigh splenocytes (right peak) in histograms for naive, PBS prime/ protein boost, LLO-LPDII DNA prime/ protein boost, and HI-LLO-LPDII DNA prime/ protein boost mice. (B) Percentage of antigen peptide (SIINFEKL)-specific cell lysis is shown. The mean of the percentage from each group was compared to that of the PBS-primed group and was statistically analyzed (n = 4; * p < 0.05)