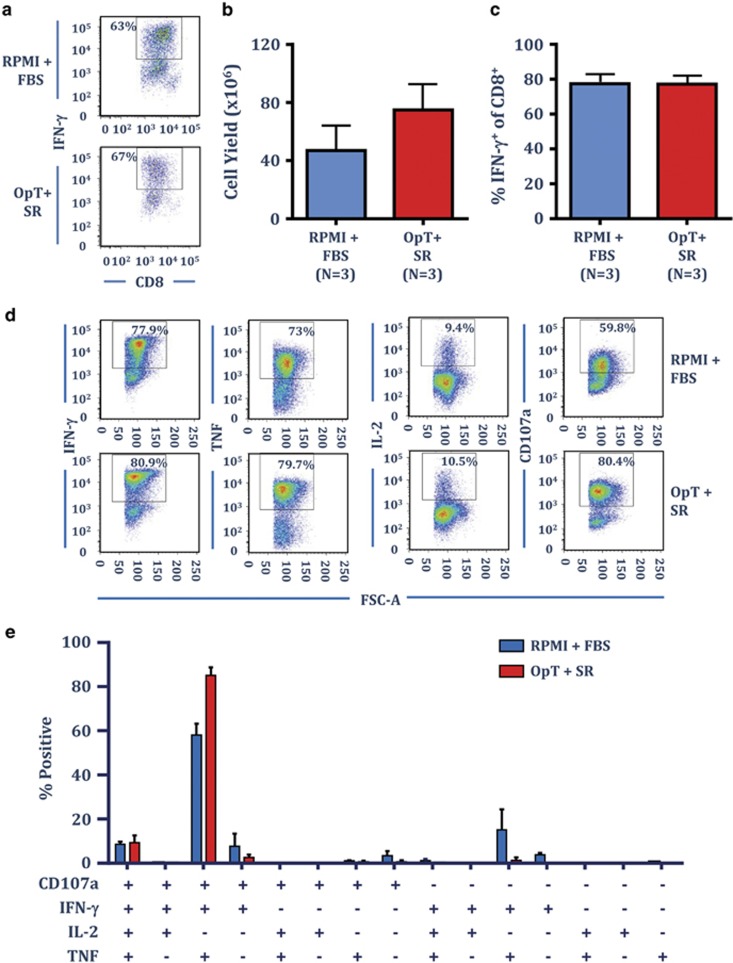
Figure 3.
CTS Immune Cell SR supports the ex vivo expansion of CMV-specific T cells. PBMC from healthy CMV-seropositive donors were cultured with autologous PBMC pulsed with a pool of CMV-encoded CD8+ T-cell peptide epitopes in either RPMI–FBS or OpTmizer-SR. T-cell cultures were supplemented with 50% fresh media containing 120 IU ml−1 IL-2 after 3 days and every 3–4 days after. On day 14, cell numbers were determined using trypan blue exclusion, then T-cell specificity was determined using an intracellular IFN-γ assay following recall with a pool of defined CMV-encoded, CD8+ T-cell peptide epitopes. (a) Representative analysis from the same donor stimulated with the CMV peptide pool and cultured in either RPMI–FBS or OpTmizer-SR is shown. (b) Data represents the mean±s.e.m. from three donors of the number of viable cells following CMV peptide pool stimulation in RPMI–FBS or OpTmizer-SR. (c) Data represent the mean±s.e.m. from three donors of the frequency of CMV-specific CD8+ T cells following CMV peptide pool stimulation in RPMI–FBS or OpTmizer-SR. (d) CMV peptide pool expanded T cells were assessed for multiple cytokine production (IFN-γ, TNF and IL-2) and degranulation (CD107a) following recall with cognate peptides. Representative dot plots are shown from the same donor cultured in either RPMI–FBS or OpTmizer-SR. (e) Data represent the mean±s.e.m. from three donors of the proportion of CMV-specific CD8+ T cells producing different combinations of IFN-γ, TNF, IL-2 and CD107a in RPMI–FBS or OpTmizer-SR.