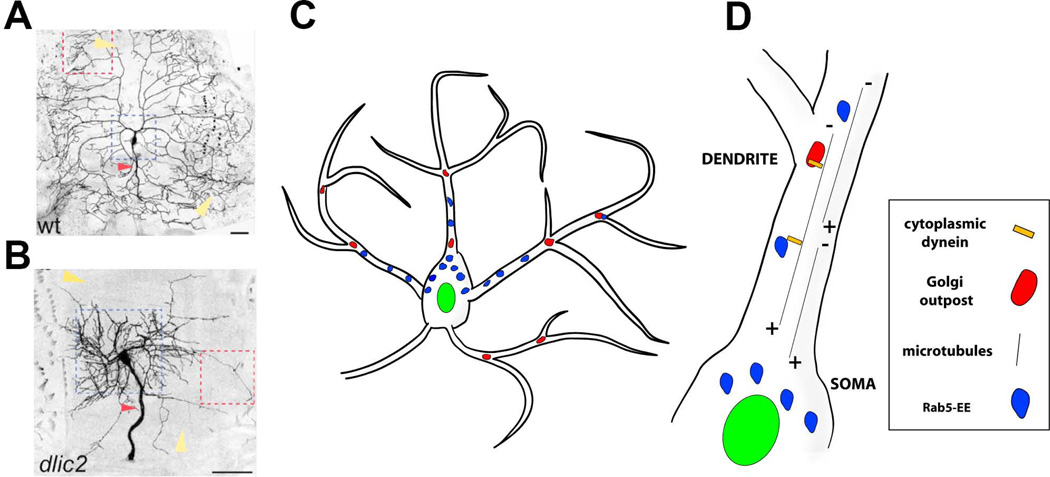
Figure 5. Molecular mechanisms that specify the location of dendritic branches along an arbor.
A, B. Images of class IV ddaC neurons that are wildtype (A) and mutant for dlic2 (B). The field size of dlic2 mutant neurons and dendritic arbors are abnormal (yellow arrowheads). The dlic2 mutant neurons show a shift in dendritic branches from distal to proximal (indicated by dotted blue squares). The red arrowheads indicate sensory axons, which are also thickened in dlic2 mutants. Reproduced with permission from Zheng et al., 2008.
C. Schematic representing Golgi outposts (red) and Rab5 early endosomes (Rab5-EE, blue).
D. Close up view of a dendritic branch indicating dynein-dependent microtubule minus (−) end directed movement of organelles to distal dendritic branches.