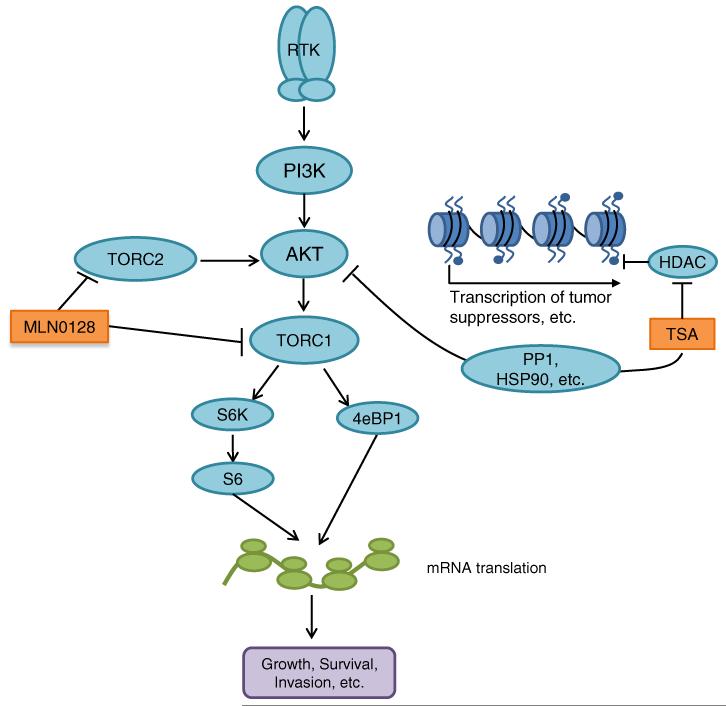
Fig. 5.
Schematic of signaling pathways targeted by MLN0128 and TSA. AKT is activated in many breast cancers through dysregulation of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and/or PI3K. MLN0128 inhibits AKT activation by inhibiting TORC2, which activates AKT. MLN0128 also inhibits signaling downstream of AKT by inhibiting TORC1. Furthermore, TSA inhibits AKT through mechanisms involving increased dephosphorylation of AKT via activation of the PP1 phosphatase or increased AKT destabilization through HSP90 inhibition. Down-regulation of AKT by MLN0128 and TSA results in decreased polyribosome function and decreased translation of mRNAs involved in carcinogenesis. TSA also induces the acetylation of histones, thus increasing the transcription of various tumor suppressors