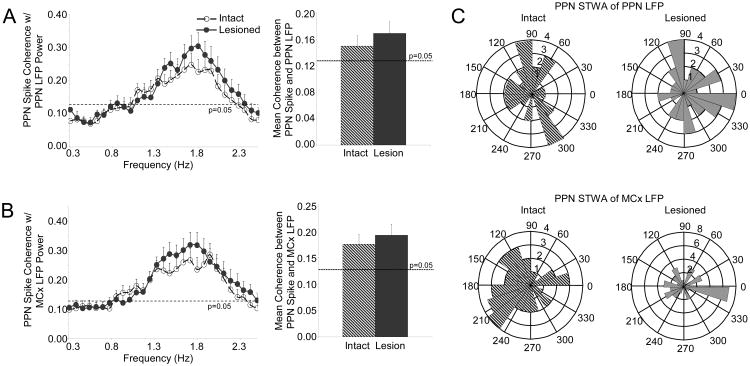
Figure 8.
Relationships between PPN spiking and LFP activity in the ketamine-anesthetized preparation. Coherence between PPN spike trains and PPN LFP (A, n=37 cells in 9 intact rats, 38 cells in 12 lesioned rats) and coherence between PPN spike trains and MCx LFP (B, n=37 cells in 9 intact rats, 38 cells in 12 lesioned rats) do not change following dopamine cell lesion. There is also no change in mean coherence between PPN spiking and PPN LFP or MCx LFP activity in the 0.3-2.5 Hz range (right). Polar histogram plots (C) summarize the distribution of phases of PPN spikes with respect to PPN LFP (top, n=38 significantly oscillatory cells in 9 intact rats, 32 cells in 12 lesioned rats) and MCx LFP (bottom, n=36 cells in 9 intact rats, 35 cells in 12 lesioned rats) oscillations. There is no consistent phase-locking between PPN spiking and LFP activity in the intact (left) or lesioned (right) rats.