Figure 1.
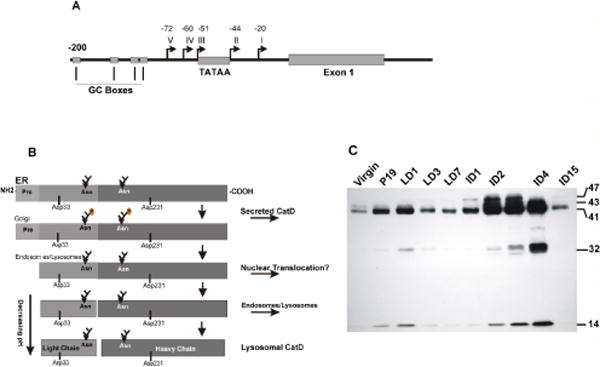
(A) Schematic presentation of CatD promoter region. The TATA and GC sequences are represented by square boxes, five transcription start sites are indicated by arrows and their distance from the +1 nucleotide are indicated. (B) Pictorial presentation of proteolytic processing of pre-pro-CatD. CatD is synthesized in the ER as a pre-pro enzyme containing a signal peptide at its amino terminus. As the enzyme traverses the ER, it loses its signal peptide and is glycosylated at two N-glycosylation sites. The pro-enzyme is transported to the Golgi, tagged with Man-6-P for binding to Man-6-PR. The complex is transported across the Golgi and reaches the endosomal compartment. The acidic environment causes the release of the receptor and the pro-peptide is cleaved generating the single chain active enzyme. Further removal of seven amino acids generates the light chain and the heavy chain mature enzyme (please see the text). (C) Developmental regulation of CatD level and proteolytic processing in mouse mammary tissue. Cytosolic extracts prepared from the mammary gland at different stages of development were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis for the presence of CatD cleavage products. V: virgin, P: pregnant, LD: lactation days 1, 3 and 7, IND: involution days 1–15. Molecular mass of CatD proteolytic products are indicated on the right.
