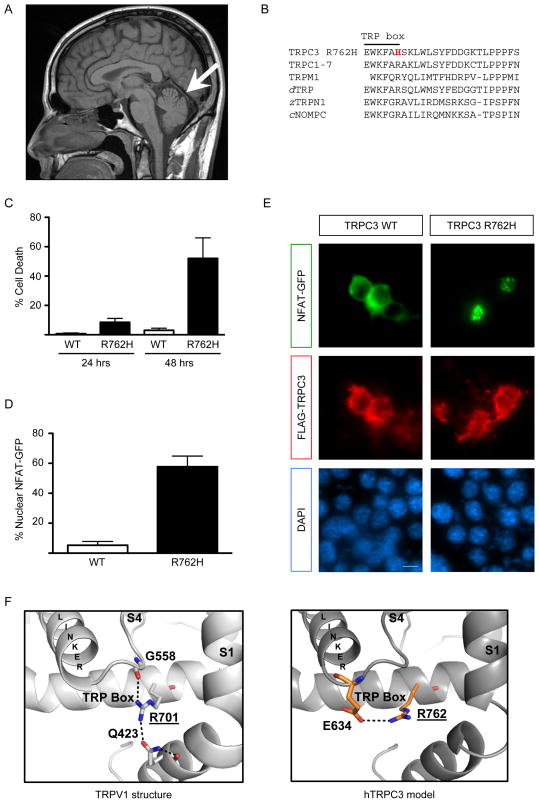
Figure. Functional analysis of TRPC3 p.Arg762His.
(A) Sagittal T1 magnetic resonance imaging of the brain shows a very mild atrophy of the cerebellar vermis (arrow) and no brainstem involvement.
(B) The TRPC3 p.Arg762His variant (R762H) lies within the TRP box (EWKFAR), part of the highly conserved TRP domain in TRP channels including all TRPCs, TRPMs (only TRPM1 shown), Drosophila dTRP, zebrafish zTRPN1, and the related C. elegans cNOMPC.
(C) Neuro-2a mouse neuroblastoma cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged TRPC3 constructs. Cells were fixed 24 or 48 hours after transfection and subjected to indirect immunofluorescence with antibodies against FLAG and the DNA dye DAPI. After 48 hours, overexpression of the p.Arg762His mutant caused significant cell death (mean + SEM; n=3; ANOVA, Bonferroni’s post-hoc test, p<0.01).
(D,E) Neuro-2a cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged TRPC3 constructs and GFP-tagged NFAT. Expression of the p.Arg762His mutant caused significant nuclear NFAT-GFP localization (mean + SEM; n=3; t-test, p<0.0005) (D). Cells were fixed 24 hours after transfection and subjected to indirect immunofluorescence with antibodies against FLAG, GFP and the DNA dye DAPI (E). Scale bar 20 μm.
(F) Structural homology modeling between the TRP box of TRPV1 (PDB ID: 3J5P) and TRPC3. TRPC3 p.Arg762 is homologous to the structurally important p.Arg701 residue in TRPV1. While the p.Arg701-interacting residues are not conserved in TRPC3, modeling suggests an interaction of p.Arg762 with the highly conserved p.Glu634 residue.