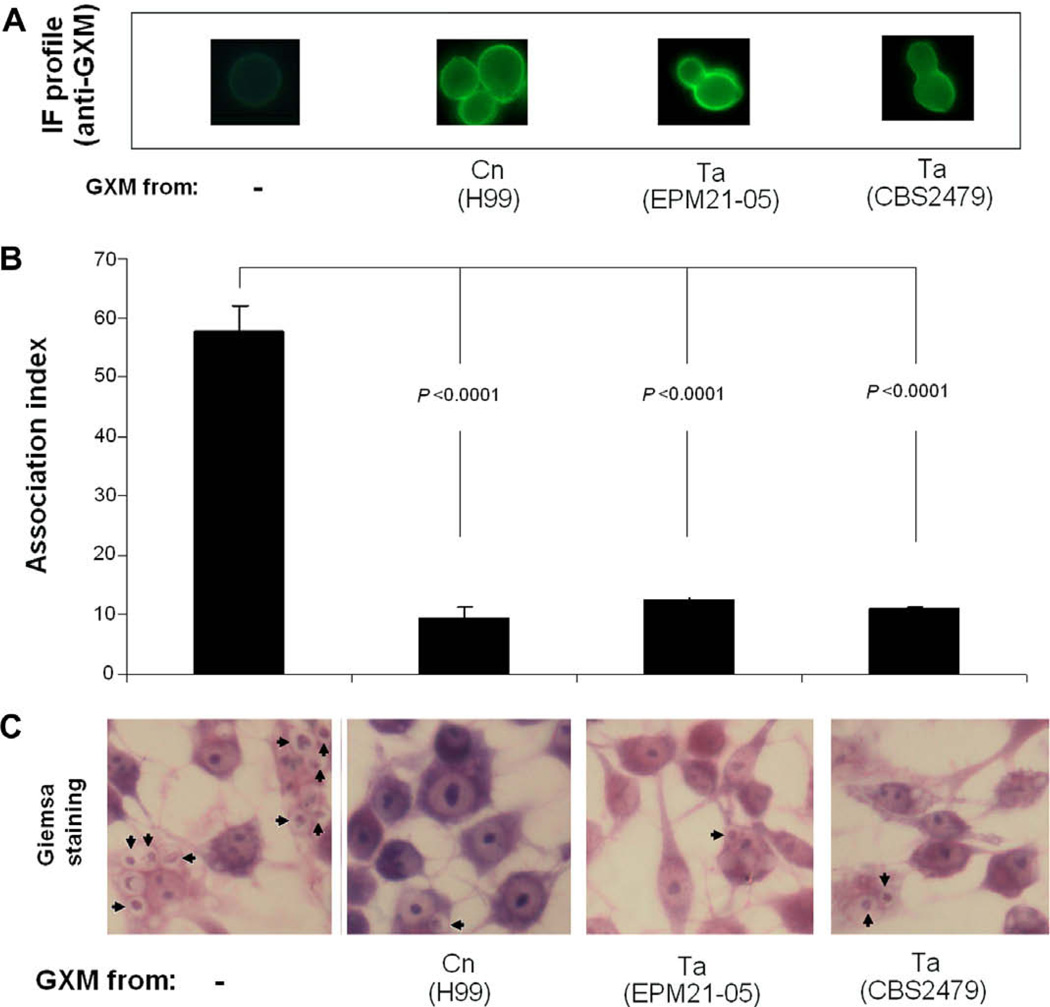
Fig. 8.
GXM from T. asahii supernatants turns acapsular mutants of C. neoformans more resistant to phagocytosis by mouse macrophages. (A) Cap67 cells were incubated in sterile medium (control, no GXM) or in the presence of culture supernatants of C. neoformans (Cn) or T. asahii (Ta). After polysaccharide incorporation, yeast cells were incubated with macrophages for determination of phagocytosis. (B) The number of phagocytes containing intracellular C. neoformans was significantly higher when yeast cells were not incubated in the presence of GXM. (C) Microscopy of Giemsa-stained, infected macrophages confirms that GXM-coated cells are more resistant to phagocytosis. Arrows indicate intracellular Cap67 cells.