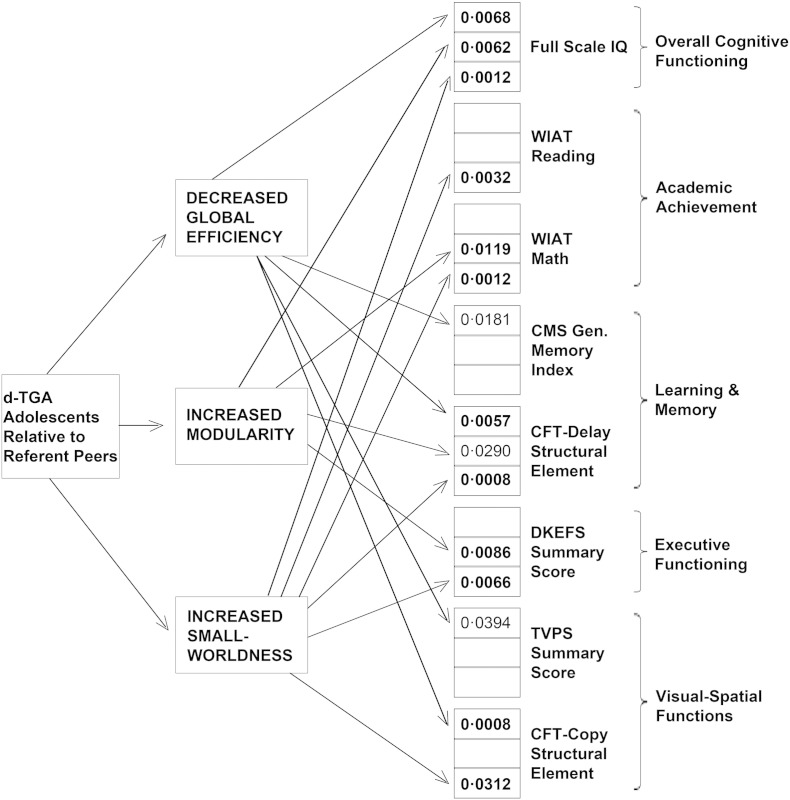
Fig. 4.
Structural network topology mediates neurocognitive differences between d-TGA adolescents and healthy referent peers. Results from the mediation analyses demonstrate different paths by which lower efficiency (less network integration) and increased modularity (more network segregation) mediate neurocognitive differences between d-TGA adolescents and healthy referent peers. Values represent significant p-values for the mediation (i.e., a × b—refer to supplement for more details). Note that p-values in bold are significant with correction for multiple comparisons (FDR < 0.05), whereas p-values in regular type are only nominally significant (p < 0.05, uncorrectEd.) See Table S1 for results pertaining to the complete list of neuropsychological tests and subtests.