Figure 1.
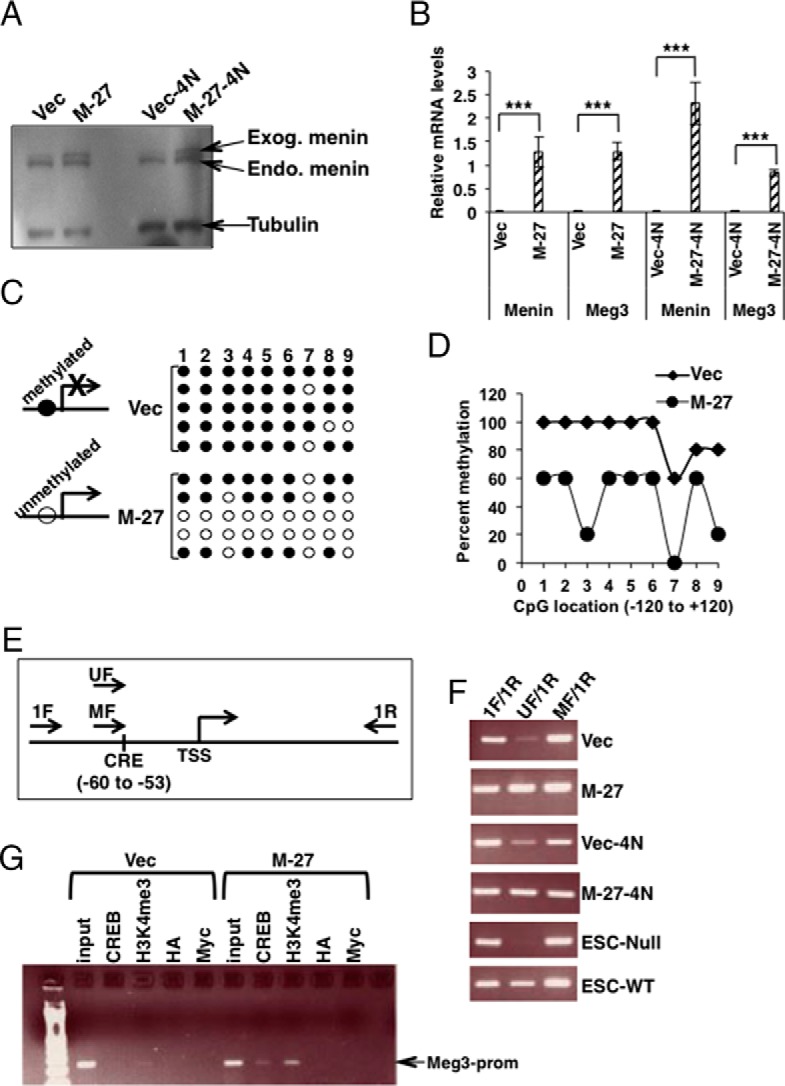
Epigenetic regulation of Meg3 by menin in MIN6 mouse insulinoma β-cells. A, Western blot detecting menin in whole-cell lysates prepared from MIN6 cell lines stably transfected with a menin-expressing plasmid [M-27 (mixed 2N+4N MIN6 cells) and M-27–4N (4N MIN6 cells)] or empty vector (Vec and Vec-4N). Tubulin was used as the loading control. Endo, endogenous menin; Exog, exogenous menin (stably transfected myc-his-tagged-menin). B, QRT-PCR assays showing significantly increased menin and Meg3 in RNA isolated from MIN6 stable cell lines shown in panel A (P < .0001). Gapdh was used as the internal control. C, Bisulfite sequencing assay of the promoter region (−120 to +120) of Meg3 using DNA isolated from MIN6 cells stably transfected with a menin-expressing plasmid (M-27) or empty vector (Vec). Reduced DNA methylation would allow Meg3 expression and increased methylation would block Meg3 expression. The numbers 1–9 indicate the nine differentially methylated CpGs in the −120 to +120 region of Meg3. Filled circles indicate methylated CpG and open circles indicate unmethylated CpG (see also Supplemental Figure 7). D, Data from panel C with significantly decreased methylation in the menin transfected MIN6 stable clone (M-27) compared with its vector control (Vec). CpG number 3 corresponds to the location of the conserved CRE site in the human and mouse Meg3 promoter. E, Schematic representation of the CRE site in the mouse Meg3 promoter and the primers for the methylation-specific PCR assay. Unmethylated (UF) and methylated (MF) primers are specific to the unmethylated and methylated CRE site, respectively. The 1F/1R primer pair spans 251 bp. The UF/1R or MF/1R primer pair spans 207 bp. TSS, transcriptional start site. F, Methylation-specific PCR assay using DNA from the indicated cell types. ESC-Null and ESC-WT are embryonic stem cells from the Men1−/− and WT mice, respectively. An increased amount of PCR product in the wells marked for UF/1R shows that exogenous menin expression in M-27 and M-27-4N unmethylates the CRE site, and the absence of the PCR product in the ESC-Null shows that, in the absence of menin, the CRE site is completely methylated. G, Agarose gel of ChIP-PCR assay with antibodies against the indicated antigens using chromatin from menin transfected MIN6 stable clone (M-27) compared with its vector control (Vec). Input corresponds to DNA isolated from chromatin used in the ChIP assay. Antihemagglutinin (HA) was used as a negative control. Anti-Myc was used to chromatin immunoprecipitate the transfected myc-his-tagged menin.
