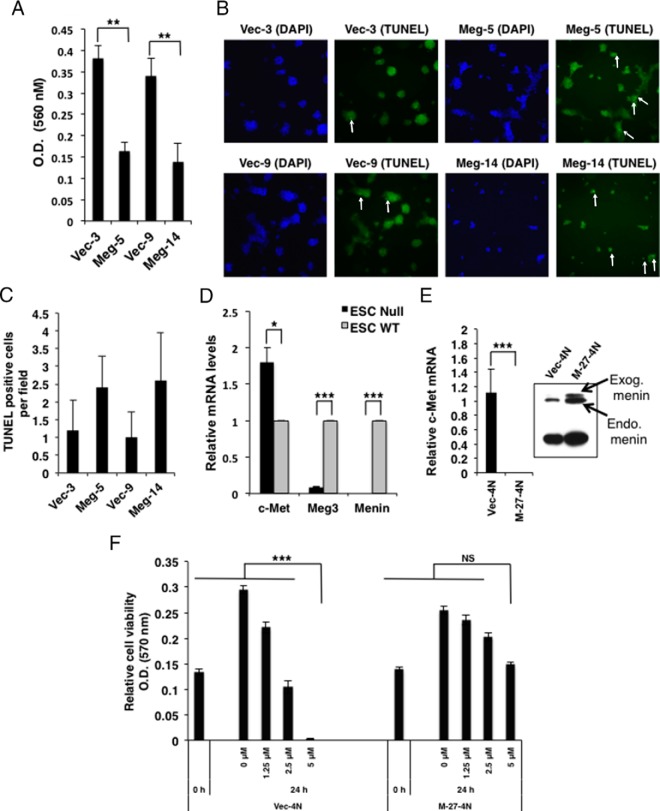
Figure 3.
Effect of Meg3 on cell migration/invasion and apoptosis and the effect of menin on c-Met. A, Cell migration/invasion assay showing decreased cell migration (represented by OD at 560 nm) in exogenous Meg3-expressing MIN6 stable cell lines (Meg-5 and Meg-14) compared with their respective vector controls (Vec-3 and Vec-9) (P < .005). B and C, Apoptosis assessed by TUNEL staining showing more apoptotic cells in exogenous Meg3-expressing MIN6 stable cell lines (Meg-5 and Meg-14) compared with their respective vector controls (Vec-3 and Vec-9) cultured in chamber slides. Representative green fluorescence images are shown (magnification, ×100), with TUNEL-positive cells indicated by white arrows (B). Nuclei were stained with 4′,6′-diamino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue) to show the location of the cells in the field. Five different fields were observed per cell line to count TUNEL-positive cells (C). D, QRT-PCR assay for c-Met using RNA isolated from ESC-Null and ESC-WT embryonic stem cells from Men1−/− and WT mice, respectively, showing significantly increased c-Met in ESC-null cells (P < .05). Gapdh was used as the internal control. E, QRT-PCR assay for c-Met using RNA isolated from the menin transfected MIN6 stable clone M-27-4N compared, with its vector control Vec-4N showing significantly reduced c-Met in M-27-4N cells (P < .0001). Gapdh was used as the internal control. Inset, Western blot for menin (upper bands): endogenous (Endo) menin in Vec-4N, and endogenous and exogenous (Exog) myc-his-tagged menin in M-27-4N. Tubulin was used as a loading control (lower band). F, Cell viability detected by an MTT assay in Vec-4N and M-27-4N before and after 24 hours of treatment with the indicated concentrations of the c-Met inhibitor PHA-665752. Significantly reduced number of cells were observed in the Vec-4N cells at 5 μM concentration of PHA-665752 (P < .0001), but no significant (NS) reduction in cell number was observed in the M-27-4N cells.