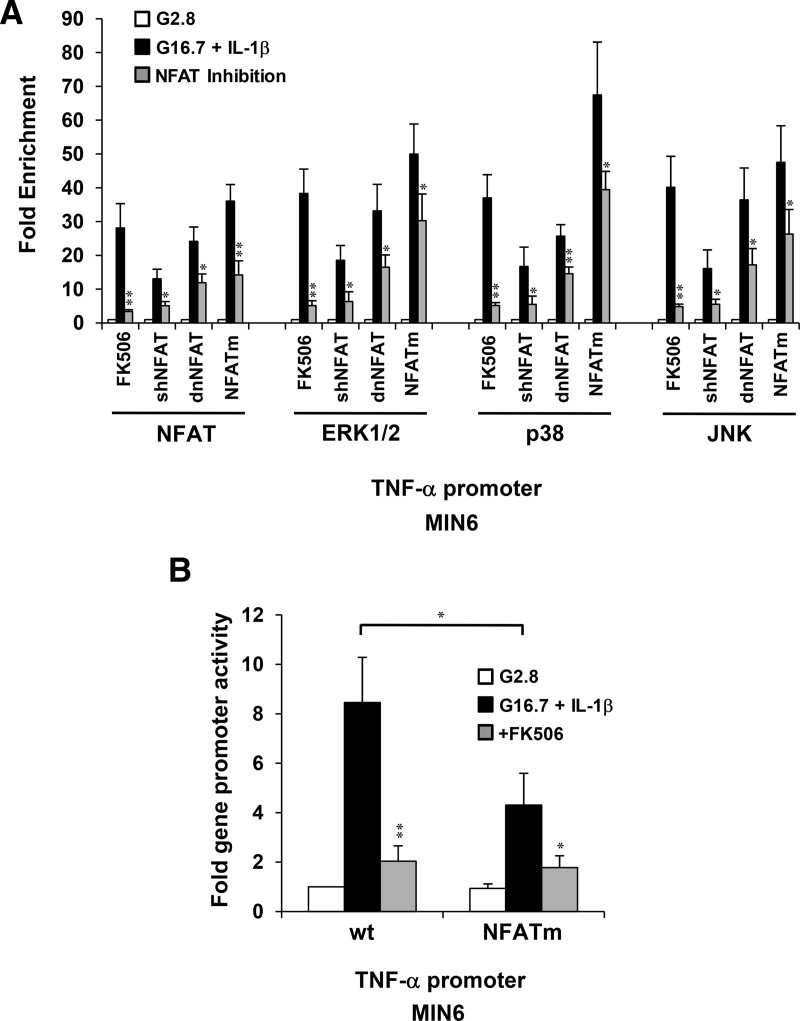
Figure 4.
NFAT mediates association of MAPKs with the TNF-α gene promoter and regulates promoter activity in response to IL-1β. A, Effects of NFAT inhibition by FK506, sh-NFAT RNAi, dnNFAT, and mutated NFAT binding site (NFATm) on fold enrichment of NFAT and MAPKs ERK1/2, p38, and JNK upon the TNF-α gene promoter with respect to 2.8mM glucose controls after 10 minutes of exposure of MIN6 cells to 16.7mM glucose and 20-ng/mL IL-1β. B, Effects of FK506 and NFATm on activation of the TNF-α gene promoter-reporter in response to 16.7mM glucose and 20-ng/mL IL-1β. Graphed results are expressed as mean ± SD determined from at least 3 independent experiments. Asterisks above bars indicate statistically significant differences (*, P < .05; **, P < .01) in mean values for treatments compared with stimulatory groups (16.7mM glucose and 20-ng/mL IL-1β) of each experimental set based on a one-way ANOVA and Dunnett's multiple comparison post hoc test. The asterisk above the bracket (B) denotes statistical significance when comparing stimulatory groups between treatments.