Figure 1.
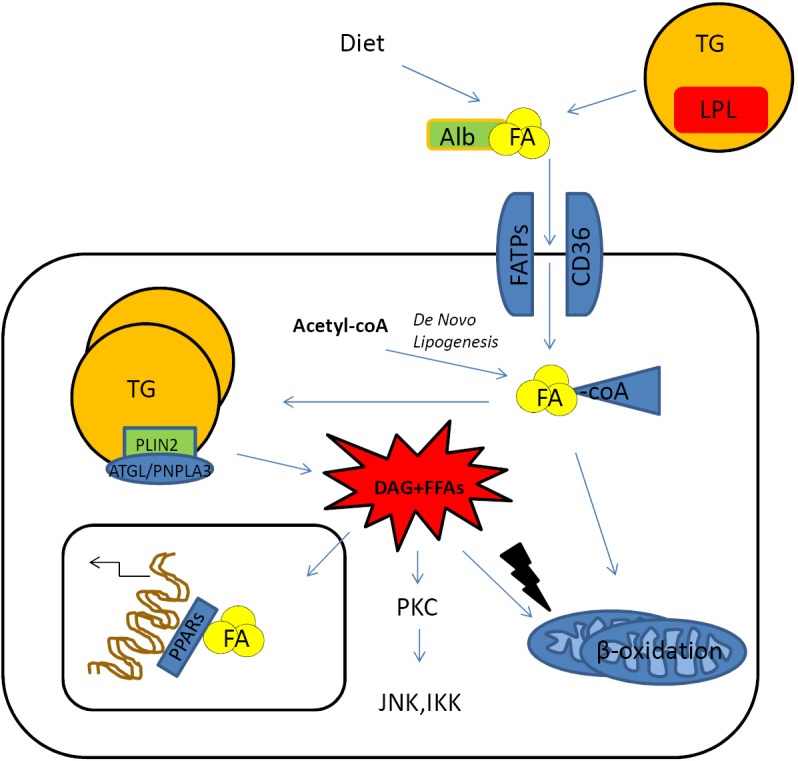
Hepatic up-take of FAs. FAs coming from diet or mobilized from peripheral storage places are usually conjugated with albumin that allows to enter the hepatocyte through specific transmembrane proteins, fatty acid transporter protein families or CD36/FAT transporter. Inside the cell, FAs originating from liponeogenesis, lipolysis or up-taken from the circulation are shuttled to several cell compartments according to the metabolic requirements. The bio-products of lipolysis such as diacylglycerol and FFAs might exert cytotoxic. Effects triggering stress signals lead to the activation of pro-inflammatory pathways (JNKs, IKKs) or increased ROS production in the mitochondrial compartment. FA, fatty acid; TG, triglycerides; PLIN, perilipins family; DAG, diacylglycerol; FFAs, free FAs; JNK, Jun-(N)-terminal kinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
