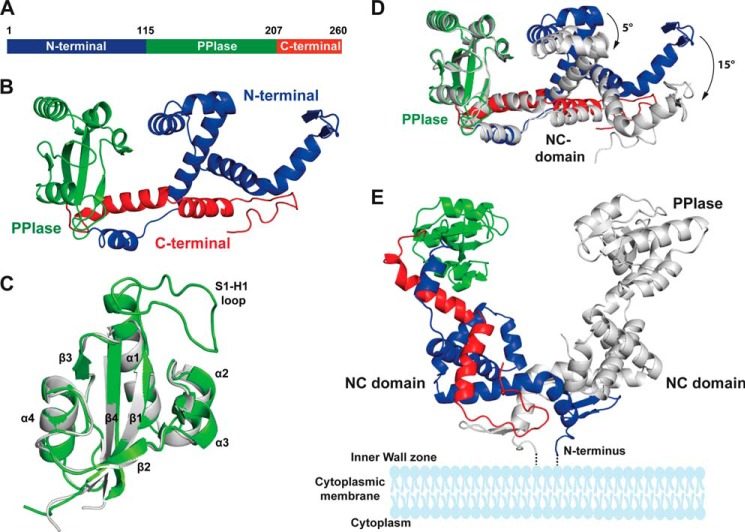
FIGURE 4.
Crystal structure of PrsA. A, schematic representation of the PrsA primary structure. B, PrsA monomer. The N-terminal domain, PPIase, and C-terminal domain are colored in blue, green, and red, respectively. C, superimposition of the parvulin domain of PrsA (gray) to the closest homologue of human Pin1 (Protein Data Bank code 1pin.pdb, green). Secondary structure elements as well as the substrate interacting loop (S1-H1) of Pin1 are indicated. D, comparison of the two PrsA molecules A and B in the asymmetric unit. PrsA molecule A is colored as in B. PrsA molecule B is shown in gray, superimposed on molecule A based on the parvulin domain. The tilt of secondary elements is indicated. E, dimeric structure of PrsA. PrsA molecules A and B are colored as in D. The estimated position of membrane and membrane anchor are indicated in schematic representation.