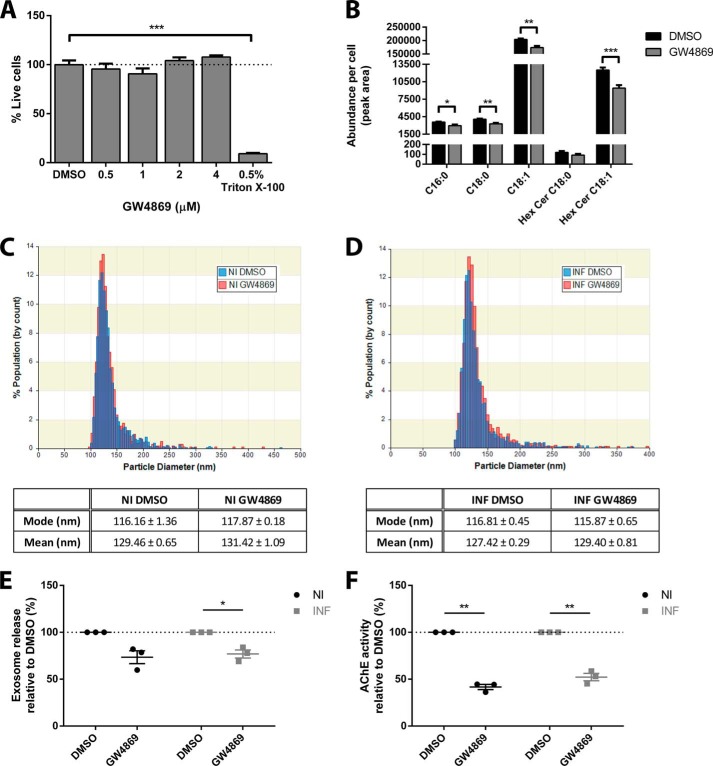
FIGURE 2.
Treatment with GW4869 impairs exosome biogenesis. A, increasing concentrations of GW4869 were tested for toxicity to GT1–7 cells, and no toxicity is observed at all concentrations tested. Note that the highest concentration tested is limited by the solubility of GW4869 and toxicity of DMSO alone to GT1–7 cells. B, GC-MS analysis of ceramide species, confirming the decrease in ceramide levels in response to GW4869 treatment. C, qNano analysis of the size distribution of exosomes in the culture supernatant of DMSO- and GW4869-treated non-infected cells and (D) prion-infected cells. E, qNano quantitation of exosomes in the culture supernatant following DMSO or GW4869 treatment, showing decreasing exosome release with GW4869 treatment. The decrease in non-infected exosomes is close to, but did not achieve statistical significance (p < 0.061). F, AChE quantitation of isolated exosomes, confirming a decrease in exosome release upon GW4869 treatment. Data presented as mean ± S.E., n = 3, *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.