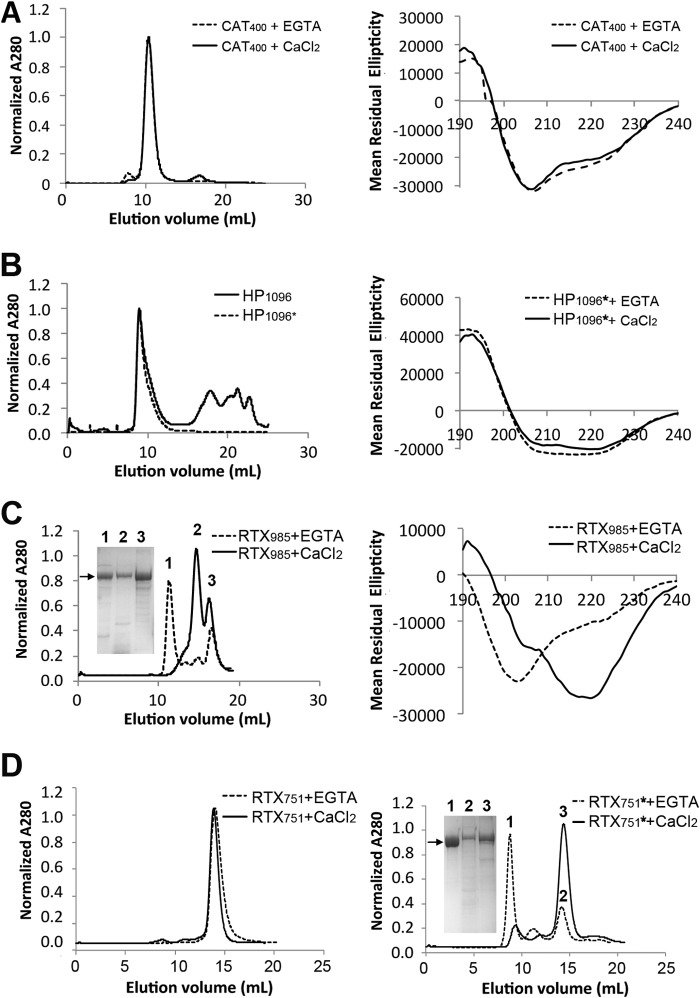
FIGURE 2.
ACT domain oligomeric state and secondary structure. Purified domains were separated by size exclusion chromatography (Superdex200 column, except Superdex75 for CAT400), with far UV circular dichroism spectra (Jasco J-815) used to assess secondary structure in the presence of 2 mm CaCl2 or the absence of calcium ions. A, catalytic domain, spanning residues 1–400 (CAT400), eluted as a single peak of expected size. The secondary structure is similar to that observed in the CAT373 crystal structure (56% helix, 14% strands, 13% turns, and 17% unordered). B, HP domain, spanning residues 399–1096, with an N-terminal MBP fusion protein eluted off SEC as high molecular weight aggregates whether acylated (*) or nonacylated. C, RTX985 formed high molecular weight aggregates in the absence of calcium ions but eluted as two peaks, one corresponding to the expected molecular mass of 78 kDa in the presence of calcium. Circular dichroism revealed significant conformational change upon addition of 2 mm CaCl2 corresponding to an increase in β-strand content. D, RTX751 domain exhibits a similar calcium-dependent delay in elution volume, which is more pronounced when the protein is acylated (*), and under these conditions it yields a single monomer peak. Inset, SDS-polyacrylamide gels show proteins present in the indicated peaks, with arrows indicating the expected monomer size.