FIGURE 4.
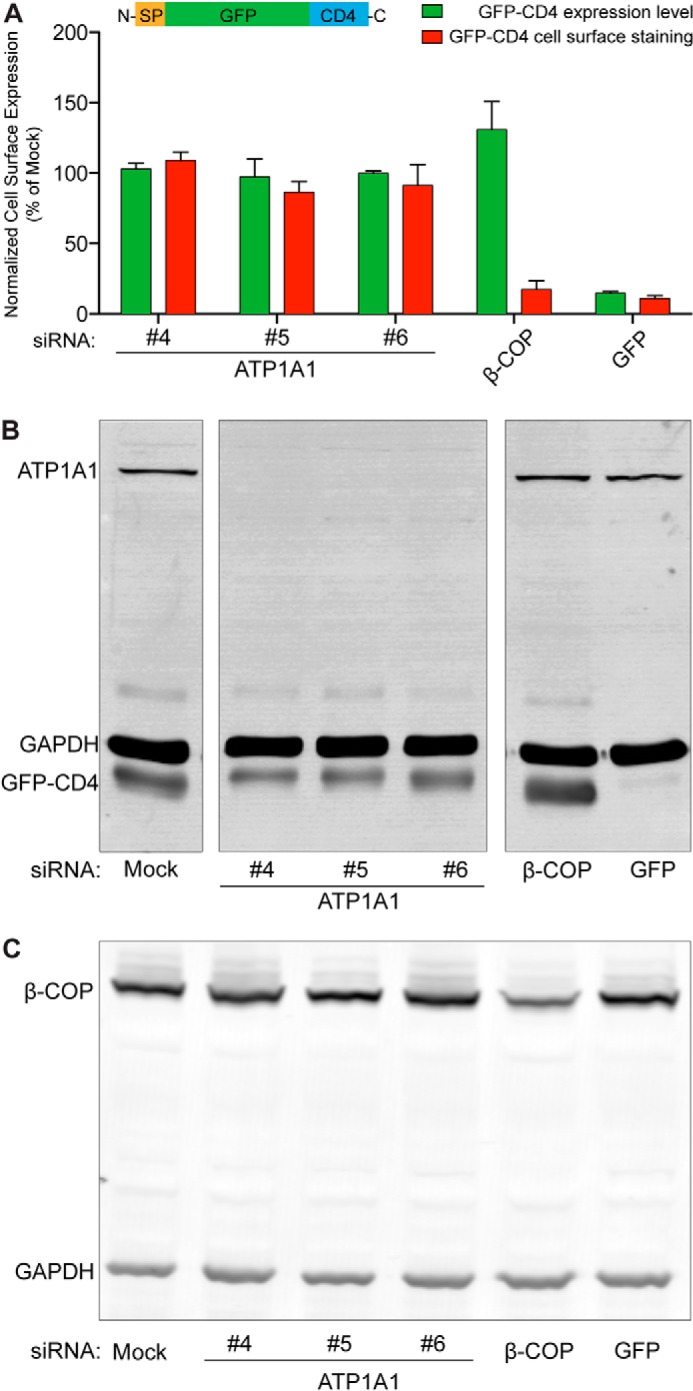
Inhibition of FGF2 secretion caused by down-regulation of ATP1A1 is not due to pleiotropic effects. A stable cell line expressing a GFP-CD4 fusion protein in a doxycycline-dependent manner was generated. This construct carries an N-terminal signal peptide and an extracellular GFP domain, followed by the transmembrane span and the cytoplasmic domain of CD4 (SP-GFP-CD4), and is transported to cell surfaces via the ER/Golgi-dependent secretory pathway. Following incubation of cells in the presence of doxycycline, GFP-CD4 was detected on cell surfaces using anti-GFP antibodies and flow cytometry. A, normalized cell surface expression of GFP-CD4 under control conditions and after down-regulation of ATP1A1 using three independent siRNAs. As a positive control, a validated siRNA directed against β-COP, a component of the coatomer complex that is essential for transport within the ER/Golgi-dependent pathway, was used (2). In addition, a siRNA directed against GFP was used to down-regulate the GFP-CD4 reporter itself. Error bars, S.D. (n = 3). B, Western blot analysis of the efficiency of down-regulation by RNA interference for ATP1A1 and GFP-CD4. C, Western blot analysis of the efficiency of down-regulation by RNA interference for β-COP.
