Figure 7.
Decreased cortical choline accompanies cortical slow-waves during partial limbic seizure.
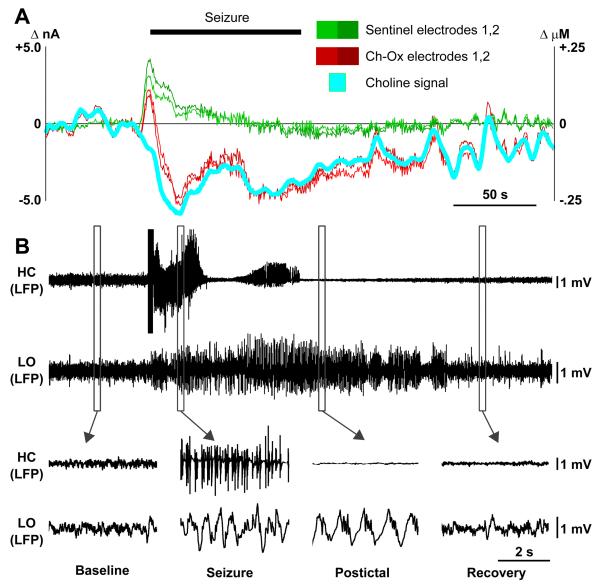
(A) Amperometric choline recordings in the cortex during partial seizure. Cyan represents the choline signal obtained by subtracting mean signal from two sentinel electrodes (Green 1,2) from mean of the two choline oxidase-coated electrodes (Red, Ch-Ox 1,2). Current is on left axis, and choline concentration on right axis obtained by in vitro choline calibration for each electrode (see also Figure S8).
(B) Simultaneous recording of partial seizure. Local field potential (LFP) signals from both hippocampus (HC) and lateral orbital frontal cortex (LO) are shown. Hippocampal seizures elicit slow oscillations in the cortex that persist postictally before recovering back to baseline (lower insets).