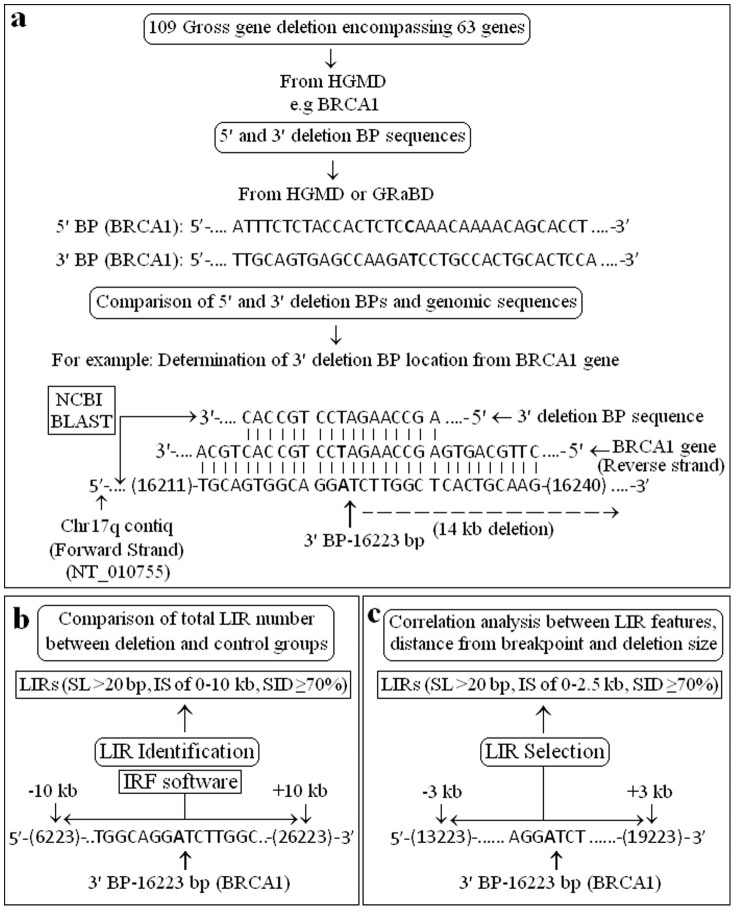
Figure 1. LIR identification and selection were performed in 218 genomic regions including 5′ and 3′ breakpoints from 109 gross deletions involving 63 human genes using IRF software.
(a) DNA sequences from 5′ and 3′ deletion BPs were obtained from HGMD and GRaBD. Each BP-DNA sequence and corresponding gene was compaired using NCBI BLAST. Deletion BP locations were determined in related genes. 3′ BP sequence from BRCA1 gene was presented for describing BLAST comparing process. (b) LIR identification was done within ±10 kb flanking sequences each of 5′ and 3′ deletion BPs and 20 kb DNA fragments from control groups using IRF. LIRs with SL > 20 bp, IS of 0–10 kb, SID ≥ 70% were included for comparing total LIR number between deletion and control groups using Mann Whitney U test. (c) LIR selection was made within ±3 kb flanking sequences each of 5′ and 3′ BPs in deletion group. LIRs with SL > 20 bp, IS of 0–2.5 kb, SID ≥ 70% were selected for analysing of correlations between LIR features, distance from breakpoint and deletion size using Pearson's coefficient. Abbreviations: Bp, base pair; BP, breakpoint; GRaBD, gross rearrangement breakpoint database; HGMD, human gene mutation database; IRF, inverted repeat finder; IS, internal spacer; kb, kilobase; LIR, long inverted repeat; SID, stem identity; SL, stem length.