Figure 5. Characterization of the acoustic field generated with the radial extracorporeal shock wave device used in the present study.
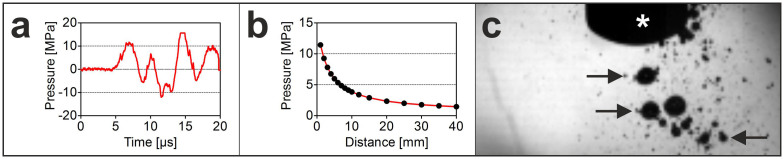
(a) Pressure as a function of time at a distance of 1 mm from the tip of the applicator. (b) Pressure as a function of the distance from the tip of the applicator (note that measurements shown in [a,b] were performed within an blown-out egg completely submerged under water using a laser fiber optic probe hydrophone). (c) Cavitation bubbles (arrows) generated during the phase of negative pressure of the radial extracorporeal shock waves, detected with a high-speed CCD camera.
