Fig. 4.
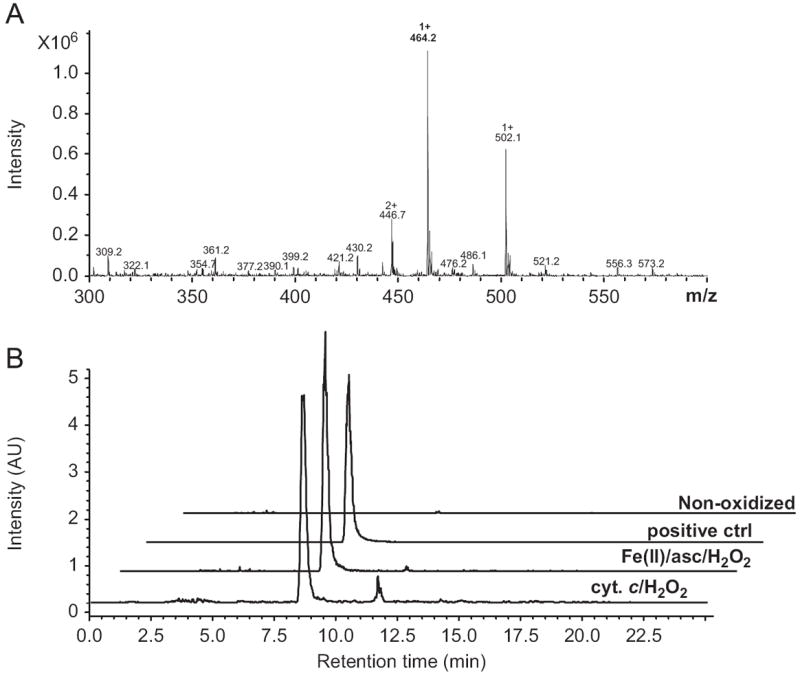
Identification of abasic site produced by cyt c. RNA oxidized by cyt c was derivatized with ARP and hydrolyzed. The hydrolysate was applied to LC/MS to identify ARP-derivatized abasic sites. As a reference, nonoxidized RNA with or without synthetic abasic sites or RNA oxidized by Fe(II)/ascorbate/H2O2 was eluted and analyzed under the same conditions. (A) The extracted ion chromatograms at 464.2 ± 0.3 m/z corresponding to ARP-abasic. (B) The mass spectra of the oxidized RNA in the presence of 20 μM/1 mM cyt c/H2O2 for 1 h at 37 °C eluted at 8.5 min.
