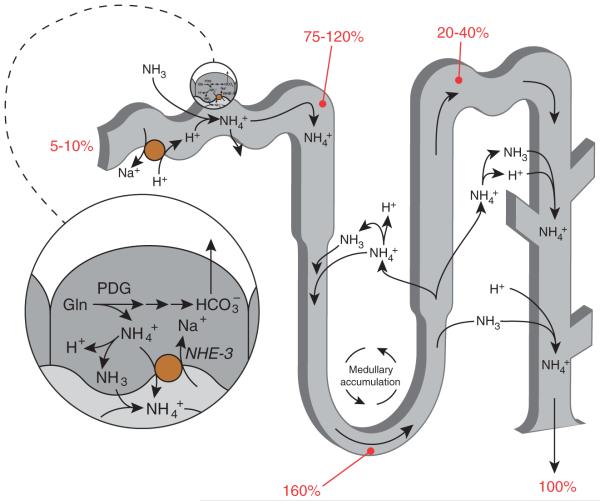
Figure 2.
Summary of renal ammonia metabolism. The proximal tubule produces ammonia, as NH4+, from glutamine. NH4+ is then secreted preferentially into the luminal fluid, primarily by NHE-3, and, in addition, there is a component of NH3 secretion. Ammonia is then reabsorbed in the thick ascending limb, resulting in ammonia delivery to the distal nephron accounting for approximately 20% to 40% of final urinary ammonia. The remaining approximately 60% to 80% of urinary ammonia is secreted in the collecting duct through parallel NH3 and H+ transport. Numbers in red indicate the proportion of total urinary ammonia present at the indicated sites under baseline conditions. Figure modified from reference (180) with permission.