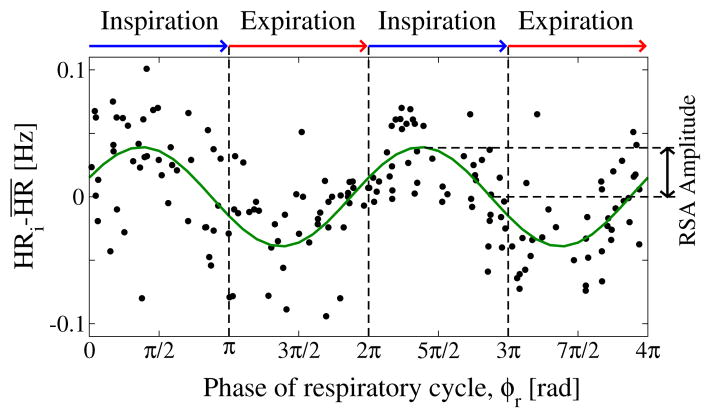
Figure 1. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia (RSA), classic form of cardio-respiratory coupling.
characterized by a periodic variation of the heart rate (HR) within each breathing cycle. The strength of the coupling is defined by the amplitude of the HR variation measured relative to the mean heart rate (RSA amplitude). Data points represent instantaneous HR, normalized to the mean within each breathing cycle, for a period of 200 sec over pairs of consecutive breathing cycles. RSA is highlighted by a sinusoidal least-square-fit line to the data points. Data are recorded from a healthy subject during deep sleep.