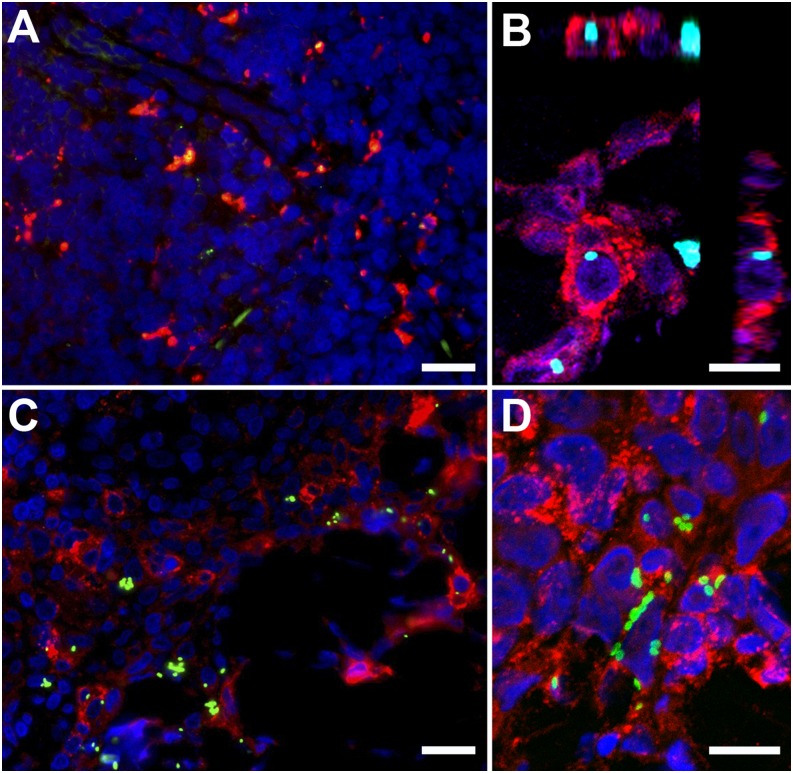
FIGURE 5.
Eschars of O. tsutsugamushi–infected cynomolgus macaques at 7 d postinfection show bacteria colocalization with APCs. Skin eschar biopsies taken at 7 d after ID inoculation of O. tsutsugamushi into the anterior thigh of cynomolgus macaques demonstrate colocalization of O. tsutsugamushi predominantly with APCs. Internalized bacteria are depicted within macrophages (A) (CD68), within APCs (B and C) (HLA-DR), predominantly in the mononuclear cell–rich infiltrates of the deeper dermis and within neutrophils (D) (lysozyme), adjacent to the necrotic center in the upper dermis. Double immunolabeling was performed with CD68 (KP1), HLA-DR, and lysozyme staining in red, and O. tsutsugamushi in green. All biopsies were taken at day 7 postinoculation. (A) NHP ID 6856. (B) NHP ID5234. (C) ID5234. (D) ID5234. Images were acquired by confocal laser-scanning microscope (Zeiss LSM 700) using AxioVision LE Software v4.8.1 (Carl Zeiss Imaging Solutions GmbH, Germany) and optimized with Photoshop CS3 extended, version 10.0. Scale bars, 20 μm (A and C); 10 μm (B and D). Original magnification ×400 (A and C), ×1000 (B and D).