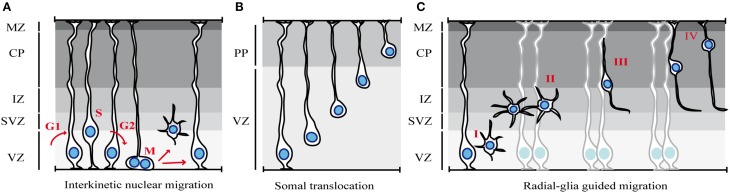
Figure 1.
Modes of migration in the cortex. (A) Interkinetic nuclear migration. The nuclei of neuroepithelial cells or radial glia cells occupy different positions along the apical-basal axis depending on the phase of the cell cycle (see text for details). (B) Somal translocation of early-born cortical neurons. Newborn neurons lose their apical attachment and reach the PP by translocation of the soma and progressive shortening of the basal process. (C) Glia-guided radial migration of cortical neurons. Four phases of radial migration can be distinguished. Newborn neurons leave the proliferative areas (I) and reach the SVZ/IZ, where they acquire a multipolar morphology (II). After pausing in the SVZ/IZ, cells migrate toward the CP, using locomotion (III). At the end of their migration, cortical neurons switch to soma translocation (IV). MZ, marginal zone; CP, cortical plate; PP, preplate; IZ, intermediate zone; SVZ, subventricular zone; VZ, ventricular zone.