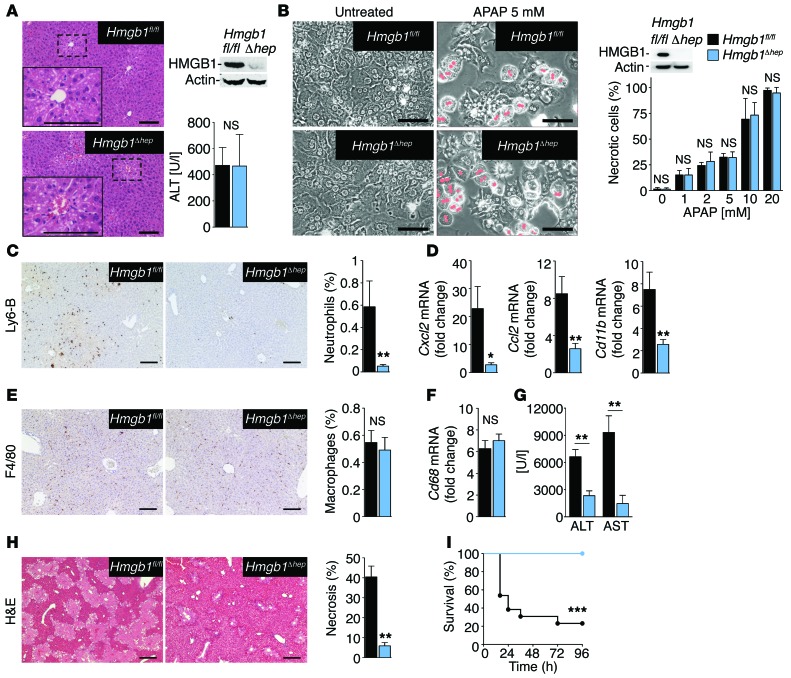
Figure 3. HMGB1 mediates neutrophil recruitment, injury amplification, and lethality following acetaminophen-induced liver necrosis.
(A) Serum ALT and liver histology in Hmgb1fl/fl (n = 8) and Hmgb1Δhep (n = 7) mice 3 hours after injection of acetaminophen (300 mg/kg). (B) Acetaminophen-induced death in Hmgb1fl/fl and Hmgb1Δhep hepatocytes (n = 3 separate isolations per group). (C–H) Hepatic neutrophil recruitment (C), inflammatory gene expression (D), macrophage numbers (E and F), serum ALT and AST (G), and liver necrosis (H) 24 hours after acetaminophen (300 mg/kg) injection in Hmgb1fl/fl (n = 8) and Hmgb1Δhep (n = 8) mice. (I) Survival after a lethal dose of acetaminophen (500 mg/kg) in Hmgb1fl/fl and Hmgb1Δhep (n = 13 per group) mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 by 2-tailed unpaired t test (A–H) and Mantel-Cox log-rank test (I). Scale bars: 200 μm (A, C, E, and H) and 100 μm (B).