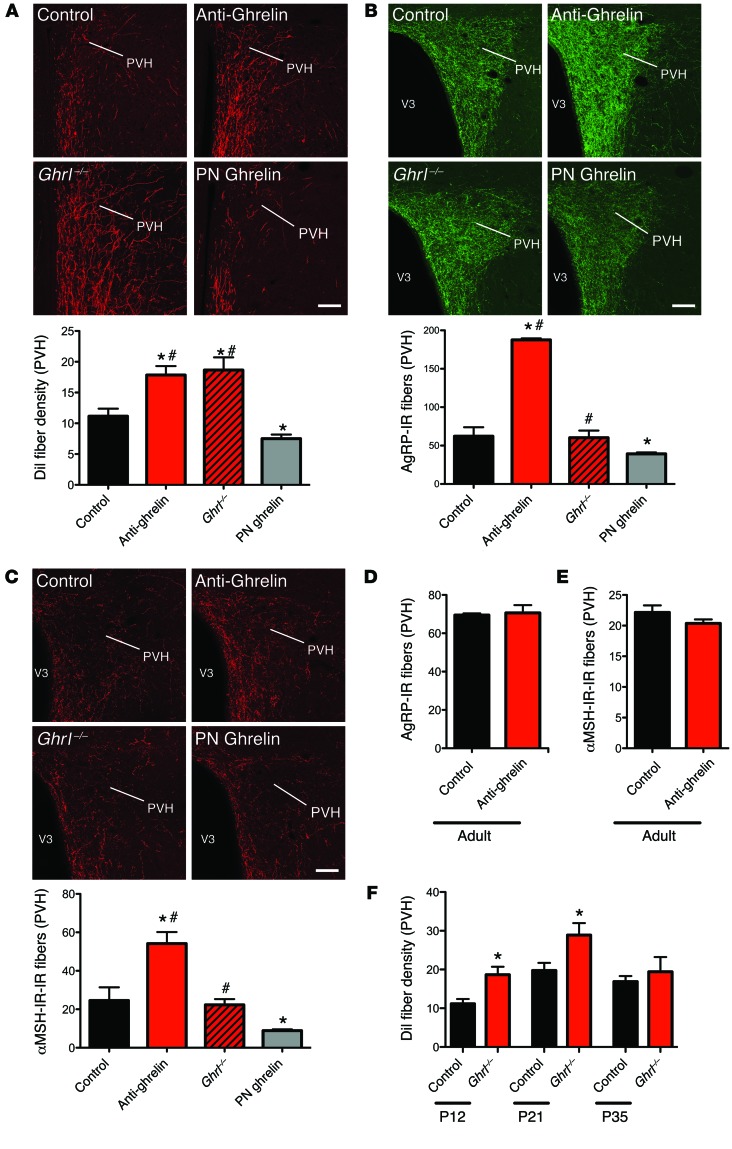
Figure 4. Neonatal ghrelin influences the normal developmental pattern of ARH neural projections.
(A) Confocal images and quantification of the density of arcuate DiI-labeled fibers innervating the PVH in P12 mouse pups injected with the control, anti-ghrelin compound, or ghrelin, and ghrelin knockout (Ghrl–/–) pups (n = 5 for control; n = 4 for Ghrl–/–; n = 6 for anti-ghrelin and PN ghrelin). (B and C) Confocal images and quantification of AgRP-IR fibers (B) and α-MSH-IR fibers (C) at 100–120 days of age in the PVH of mice neonatally injected with the control or anti-ghrelin compound, mice neonatally injected with ghrelin, and Ghrl–/– mice (n = 6 for control, Ghrl–/–, and PN ghrelin; n = 7 for anti-ghrelin). (D and E) Quantification of AgRP-IR (D) and α-MSH-IR (E) fibers at 100–120 days of age in the PVH of mice injected with control or anti-ghrelin during adult life (n = 3 per group). (F) Quantification of the density of arcuate DiI-labeled fibers innervating the PVH in P12, P21, and P35 control and ghrelin knockout (Ghrl–/–) mice (n = 5 for control; n = 4 for P12 Ghrl–/–; n = 6 for P21 and P35 Ghrl–/–).Values are shown as the mean ± SEM. V3, third ventricle. *P < 0.05 vs. control; #P < 0.05 vs. PN ghrelin. Statistical significance was determined using 2-tailed Student’s t tests (D and E) and a 2-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc test (A, B, C, and F). Scale bars: 150 μm.